Biomes and Ecosystems  By Trista L. Pollard 3.6.F. Ecology 1. Give reasons supporting the fact that the number of organisms an environment can support depends on the physical conditions and resources available. a. Explain that populations increase or decrease relative to the availability of resources and the conditions of the environment. b. Identify and describe factors that could limit populations within any environment, such as disease, introduction of a nonnative species, depletion of resources, etc. c. Explain that within any environment organisms with similar needs may compete with one another for resources. d. Cite examples to illustrate that competition is reduced when organisms use different sets of resources, such as birds in a forest eat different kinds and sizes of seeds. Vocabulary Words to Look up and put in your Journal Abiotic Biotic Ecology Ecosystem Habitat Niche PopulationSize Limiting Factor Community Native Species Exotic Species Predation Predator Prey Symbiosis Commensalism Mutualism Parasitism Competition Adaptation PRE -TEST Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this pretest about Biomes
PRE -TEST Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this pretest about food webs
BIG IDEAS 1. Ecology is the study of how living things interact with each other and their environment. Ecologist study how the biotic and abiotic factors interact within an ecosystem. 2. An ecosystem is all the living things and nonliving things that interact in an area. 3. The living parts of an ecosystem are called biotic factors. 4. The non-living factors of an ecosystem are called abiotic factors. Abiotic factors found in many environments include water, sunlight, oxygen, temperature, and soil. 5. Habitat is place where an organism lives and that provides the things the organisms needs. 6. Population referred to all the organisms of one species in a particular area. 7. All the different populations that live together in an area make up a community. 8. Several communities make up an ecosystem. 9. Some limiting factors for populations are food, space, and weather conditions. 10. Other factors that could limit populations within any environment include: disease, introduction of a nonnative species, depletion of resources, etc. 11. The major types of interactions among organisms are competition, predation, and symbiosis. 12. Organisms compete for space, food, and water. 13. Competition is reduced when organisms use different sets of resources. 14. The number of organisms an environment can support depends on the physical conditions and resources available. 15. If the birth rate of a population is greater than the death rate the population’s size increases. If death rate is greater than birth rate the population’s size decreases. 16. Populations increase or decrease relative to the availability of resources and the conditions of the environment. 17. If predators are effective the prey population decreases, but a decrease in prey population in turn affects the predator population. 18. Within any environment organisms with similar needs may compete with one another for resources. 19. An organism’s particular role or how it makes its living is called its niche. 20. When one organism consumes another it is called predation. Predators kill, prey is eaten. 21. Predators and prey often have adaptations to help them kill or help them not be eaten (hide, run away, etc.) 22. Symbiosis is a close relationship between two species that benefits at least one species. There are three types of symbiotic relationships: mutualism (both species benefit), commensalism (one species benefits and other is not harmed), and parasitism (one species benefits and other is harmed). Assignment=Please watch this video below and write between 10-20 notes from it in your journal. Vocabulary Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this activity by Completing each sentence using the words in the word list.
 1 Did you know that there are communities right in your backyard? Do you know that some communities don't have houses, but trees, plants, and shrubs? Well, these communities are part of ecosystems . They are also part of biomes . 1 Did you know that there are communities right in your backyard? Do you know that some communities don't have houses, but trees, plants, and shrubs? Well, these communities are part of ecosystems . They are also part of biomes .2 Biomes are large areas that have similar plants, animals, and other organisms . Organisms are living things that can work independently. Some of these organisms we cannot see with our eyes. However, they are there. Ecosystems are smaller than biomes. They are a community of plants and animals that live in an environment. Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above 3 There are many biomes on Earth. However, we will only talk about four. They are forests, grasslands, deserts, and tundras. The animals and plants in these biomes need to adapt to the environment. Each biome has different types of water, soil, and climate. 4 Forests are trees and other plants that cover a large area. These trees and plants grow in groups that are very dense. Depending on the climate, different types of trees and plants grow in the forest. There are tropical rainforests, tropical dry forests, cold climate forests, and temperate forests. Temperate forests are found in the eastern United States. These forests have cold winters and warm summers. You can tell you are in a temperate forest if the leaves change colors in the fall. Cold climate forests have trees that have cones. You would find pine, fir, and spruce trees in these areas. These forests are found in the mountains. Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above 5 Tropical forests are found in different areas of the world. Tropical dry forests are found in parts of Australia and Central America. They have high temperatures. They also have very little rainfall. Tropical rainforests are the opposite. They have a lot of rain. Some of these forests are found in Africa, South America, and Asia. Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above 6 Grasslands are areas that are covered with grass and very few trees. You know them as prairies in the United States. There are very hot summers and very cold winters in grassland areas. Grasslands have some rain. However, the rain is not enough for trees to grow there. Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above 7 Assignment=Please watch this video below and write between 10-20 notes from it in your journal. Deserts are the driest places on Earth. They have very little rain during the year. The plants that are in the desert have to survive the low amount of rain. You may see cacti in deserts. The U.S. has a desert in California. It is called the Mojave Desert (Mo-ha-vee). The Sahara Desert in Africa is the largest desert on Earth. Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above Assignment=Please watch this video above and write between 10-20 notes from it in your journal. The last biome is tundra. A tundra is a frozen prairie. If you were to visit Antarctica or Alaska, you would be visiting a tundra. Tundras have summers that are not very hot. The winters are extremely cold. There are plants that grow in the tundra. However, there are not any trees. Assignment=Please watch this video above and write between 10-20 notes from it in your journal. 9 Animals that live in these different biomes need to adapt to the climate. Their feeding habits may depend on the climate. They may have layers of fur that help to keep them warm. They may also have very thin fur or covering for hot weather. 10 Ecosystems can be very small or very large. They can be as large as the Amazon Rainforest. They can also be the small log in your backyard. The ants in your backyard are part of an ecosystem. They depend on the water from the rain. They use the soil to make their homes. If we drop food in the backyard, it becomes their food. They live together with the other insects and animals. 11 So take a trip into your backyard or to the park in your neighborhood. There is an ecosystem waiting for you to explore. Copyright © 2011 edHelper Assignment=Please copy this activity in your journal and complete each sentence using the words in the word list.
Biomes and Ecosystems CLOZE Activity Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this activity there |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Did you know that there are communities right in your backyard? Do you know that some(1) _______________________ don't have houses, but trees, plants, and shrubs? Well, these communities are part ofecosystems . They are also part of biomes .
Did you know that there are communities right in your backyard? Do you know that some(1) _______________________ don't have houses, but trees, plants, and shrubs? Well, these communities are part ofecosystems . They are also part of biomes .Biomes are large areas that have similar plants, animals, and other organisms . Organisms are living things that can work independently. Some of these organisms we cannot see with our eyes. However, they are there. Ecosystems are smaller than biomes. They are a (2) _______________________ of plants and animals that live in an environment.
There are many (3) _______________________ on Earth. However, we will only talk about four. They are forests,(4) _______________________ , deserts, and tundras. The animals and plants in these biomes need to (5) _______________________ to the environment. Each biome has different types of water, soil, and climate.
Forests are trees and other plants that cover a large area. These trees and plants grow in groups that are very(6) _______________________ . Depending on the climate, different types of trees and plants grow in the forest. There are tropical rainforests, tropical dry forests, cold climate forests, and temperate forests. Temperate forests are found in the eastern United States. These forests have cold winters and warm summers. You can tell you are in a (7) _______________________ forest if the leaves change colors in the fall. Cold climate forests have trees that have cones. You would find pine, fir, and spruce trees in these areas. These forests are found in the mountains.
Tropical forests are found in different areas of the world. Tropical dry forests are found in parts of Australia and Central America. They have high temperatures. They also have very little (8) _______________________ . Tropical rainforests are the opposite. They have a lot of rain. Some of these forests are found in Africa, South America, and Asia.
Grasslands are areas that are covered with grass and very few trees. You know them as prairies in the United States. There are very hot summers and very cold winters in (9) _______________________ areas. Grasslands have some rain. However, the rain is not enough for trees to grow there.
Deserts are the driest places on Earth. They have very little rain (10) _______________________ the year. The plants that are in the desert have to survive the low amount of rain. You may see cacti in deserts. The U.S. has a desert in California. It is called the Mojave Desert (Mo-ha-vee). The Sahara Desert in Africa is the largest desert on Earth.
The last (11) _______________________ is tundra. A tundra is a frozen prairie. If you were to (12) _______________________ Antarctica or Alaska, you would be (13) _______________________ a (14) _______________________ .(15) _______________________ have summers that are not very hot. The winters are (16) _______________________ cold. There are plants that grow in the tundra. However, there are not any trees.
Animals that live in these (17) _______________________ biomes need to adapt to the climate. Their feeding habits may depend on the climate. They may have layers of fur that help to keep them warm. They may also have very thin fur or covering for hot weather.
(18) _______________________ can be very small or very large. They can be as large as the Amazon Rainforest. They can also be the small log in your backyard. The ants in your backyard are part of an ecosystem. They depend on the water from the rain. They use the soil to make their homes. If we drop food in the backyard, it becomes their food. They live together with the other insects and animals.
So take a trip into your backyard or to the park in your (19) _______________________ . There is an(20) _______________________ waiting for you to explore.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Vocabulary
|
30. | Mosses can have a ____ relationship with trees. | |
31. | Is the wolf considered a ____. | |
32. | A special way that animals live together is called a ____. | |
33. | The frog looked at its ____ through its yellow peepers. | |
34. | Orchids are another plant that can have a ____ relationship with a tree. | |
35. | One ____ sea turtles have is to hide their eggs in the sand. | |
36. | The class has several forms of life represented in it. It's a type of ____. | |
37. | The snails gravitate toward the moist, dark area of the ____. | |
38. | An oak tree and the organisms tht inhabit it can be thought of as a small ____. | |
39. | Bees have an important ____ in pollinating flowers as they gather nectar to make honey. | |
40. | The ____ ate his prey. | |
41. | A tapeworm living inside a human descrbes a ____ relationship. | |
42. | In ____, the parasite usually lives on or in a much larger organism and feeds on it while it is still alive. | |
43. | My cousin, Jordan, won a medal at the track ____. |
Assignment=Please watch this video above and write between 10-20 notes from it in your journal.
Symbiosis
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this activity there
Complete each sentence using the words in the word list.
|
44. | The ____ of the aquarium consists of the eggs, fish , and gravel. | |
45. | ____ parts of an ecosystem include the plants and animals in that area. | |
46. | Phytoplankton are the main source of the ocean's food chain and energy source for the marine ____. | |
47. | An envirionment needs both ____ and abiotic factors. | |
48. | A forest is a land ____. | |
49. | The thick fur of some animals is an ____ to cold environments. | |
50. | The professional pool player used his own cue in the ____. | |
51. | The fox is a ____ of mice and voles. | |
52. | My cousin, Matthew, won a medal at the track ____. | |
53. | Animals on the Galapagos are known for their ____ to their habitat. | |
54. | A bear's ____ is the woods. | |
55. | The African Savanna is the lion's ____. | |
56. | Hibernation is a behavioral ____ that helps some animals survive the winter, when food supplies are low. | |
57. | The reintroduction program was a success because the young birds were released back into their natural ____ and survived. | |
58. | Birds of ____ use their talons to catch their dinner. |
BIOME GAME
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this pretest about food webs
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
FOOD WEB
| Food Webs By Cindy Grigg |  |
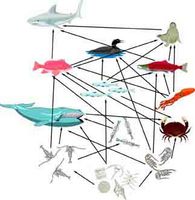 1 Every living thing needs food. People enjoy eating food. But that's not the reason we eat. People eat to stay alive. We need food so we can grow. We need food for the energy to do things. Our bodies change our food into energy. We use energy when our hearts beat. We use energy when our lungs breathe. We need energy to stay alive. We use the energy to walk, talk, read, sleep, think, and dream.
1 Every living thing needs food. People enjoy eating food. But that's not the reason we eat. People eat to stay alive. We need food so we can grow. We need food for the energy to do things. Our bodies change our food into energy. We use energy when our hearts beat. We use energy when our lungs breathe. We need energy to stay alive. We use the energy to walk, talk, read, sleep, think, and dream.2 Just like us, animals of all kinds need food, too. Food and its energy move from one living thing to another. In the ocean, big fish eat little fish. Little fish eat smaller animals or plants that live in the ocean. Food and energy move in a path we call the food chain. It's usually not a straight path. There can be links between many different things. If we draw a picture of the path that food's energy moves in, it begins to look more like a spider web. So the food chain is often called the food web, too. A food web is a diagram or drawing that shows how living things get energy.
3 The food of almost every living thing begins with sunlight. Green plants can use sunlight to make their own food. Even plants that live in the ocean do this. Some of the smallest living things in the ocean are algae. They are so simple they are not even called plants. Algae don't have roots or stems. They don't even have true leaves. Many of them can't be seen without a microscope. Just because they're so small we can't see them doesn't mean they aren't important. These tiny, floating living things are very important! They use sunlight to make their own food. As they do this, they make oxygen for us and all animals on Earth to breathe.
4 Algae are food for tiny little floating animals. Together the floating algae and animals are called plankton. Plankton is food for all kinds of animals that live in the ocean. Krill are small shrimp-like animals that live in the ocean. Krill eat plankton. Many animals eat krill. Let's say a seal eats the krill. Then a killer whale might come along and eat the seal. If we were drawing this food chain, we would start with sunlight. Plankton would be the next link in the chain. Then krill comes next because krill eat plankton. The seal would be the next link. Then the killer whale is next. We say the killer whale is at the top of the food chain.
5 Sooner or later the killer whale will die. At least some of its body will sink to the ocean floor. Tiny living organisms will feed on the remains. The food and energy stored in the killer whale's body will now go to feed the tiny organisms, and the cycle of the food chain will start over.
6 But krill eat other things besides plankton. And killer whales don't just eat seals. Most animals don't just eat one type of food. Most animals aren't just eaten by one type of predator, either. Predators hunt, kill, and eat other animals. The animals they hunt are calledprey. Carnivores are animals that eat the meat of other animals. Herbivores are animals that eat only plants. Animals that eat both plants and animals are called omnivores. The chain becomes a web, with many different animals feeding on others. Krill is food for seabirds, whales, and penguins, too. Krill is a part of many food webs.
Assignment= Please copy his graphic organizer into your journal and complete it from the reading above
7 Each living thing has its special place in the food web. This place is called their niche. Green plants and algae that make their own food using energy from the sun are called producers. Living things that feed on producers are called consumers. Consumers cannot make their own food. Decomposers, like fungi and bacteria, break down the remains of dead organisms and their wastes. For example, a dead tree rots. Bacteria and fungi break down the remains of the dead tree. Nutrients are returned to the soil. Then trees living nearby absorb the nutrients and use them to stay alive and grow. Matter that is no longer living is recycled by decomposers. Each animal has a special place in its community of plants and animals. A community is a place where plants and animals interact with the environment. Almost every living thing becomes food for another living thing. We are all linked in a web of energy that passes from one living thing to another.
Assignment= Please copy his graphic organizer into your journal and complete it from the reading above
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Food Webs
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
Food Webs
|
| ||||
|
|
Food Webs
Food Webs
Food Webs
| Food Webs By Cindy Grigg |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Every living thing needs food. (1) _______________________ enjoy eating food. But that's not the(2) _______________________ we eat. People eat to stay alive. We need food so we can grow. We need food for the energy to do things. Our bodies change our food into energy. We use energy when our hearts beat. We use energy when our lungs breathe. We need energy to stay alive. We use the energy to walk, talk, read, sleep, think, and(3) _______________________ .
Every living thing needs food. (1) _______________________ enjoy eating food. But that's not the(2) _______________________ we eat. People eat to stay alive. We need food so we can grow. We need food for the energy to do things. Our bodies change our food into energy. We use energy when our hearts beat. We use energy when our lungs breathe. We need energy to stay alive. We use the energy to walk, talk, read, sleep, think, and(3) _______________________ .Just like us, animals of all kinds need food, too. Food and its energy move from one living thing to another. In the ocean, big fish eat little fish. Little fish eat smaller animals or plants that live in the ocean. Food and energy move in a path we call the food chain. It's usually not a straight path. There can be links between many different things. If we draw a picture of the path that food's energy moves in, it begins to look more like a spider web. So the food chain is (4) _______________________ called the food web, too. A food web is a diagram or drawing that shows how living things get energy.
The food of almost every living thing begins with sunlight. Green plants can use sunlight to make their own food. Even plants that live in the ocean do this. Some of the smallest living things in the ocean are algae. They are so (5) _______________________ they are not even called plants. Algae don't have (6) _______________________ or stems. They don't even have true leaves. Many of them can't be seen without a(7) _______________________ . Just because they're so small we can't see them doesn't mean they aren't important. These tiny, floating living things are very important! They use sunlight to make their own food. As they do this, they make oxygen for us and all animals on Earth to breathe.
Algae are food for tiny little floating animals. Together the floating algae and animals are called plankton. Plankton is food for all kinds of animals that live in the ocean. Krill are small (8) _______________________ animals that live in the ocean. Krill eat plankton. Many animals eat krill. Let's say a seal eats the krill. Then a (9) _______________________ whale might come along and eat the seal. If we were drawing this food chain, we would start with sunlight. Plankton would be the next link in the (10) _______________________ . Then krill comes next because krill eat plankton. The seal would be the next link. Then the killer whale is next. We say the killer whale is at the top of the food chain.
Sooner or later the killer whale will die. At least some of its body will sink to the ocean floor. Tiny living organisms will feed on the remains. The food and energy stored in the killer whale's body will now go to feed the tiny organisms, and the cycle of the food chain will start over.
But krill eat other things (11) _______________________ plankton. And killer whales don't just eat seals. Most animals don't just eat one type of food. Most animals aren't just eaten by one type of predator, either. Predators hunt, (12) _______________________ , and eat other animals. The animals they hunt are called prey. Carnivores are animals that eat the meat of other animals. Herbivores are animals that eat only plants. Animals that eat both plants and animals are called omnivores. The chain becomes a web, with many different animals feeding on others. Krill is food for seabirds, whales, and penguins, too. Krill is a part of many food webs.
Each living thing has its special place in the food web. This place is called their niche. Green plants and algae that make their own food using energy from the sun are called producers. Living things that feed on producers are called consumers. Consumers cannot make their own food.(13) _______________________ , like fungi and bacteria, break down the remains of dead organisms and their wastes. For example, a dead tree rots. Bacteria and fungi break down the remains of the dead tree. Nutrients are returned to the soil. Then trees living nearby absorb the nutrients and use them to stay alive and grow. Matter that is no longer living is recycled by decomposers. Each animal has a special place in its(14) _______________________ of plants and animals. A community is a place where plants and animals interact with the(15) _______________________ . Almost every living thing becomes food for another (16) _______________________ thing. We are all linked in a web of energy that passes from one living thing to another.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this test about food webs there
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
| What Is Energy? By Patti Hutchison |  |
 1 Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Every living thing needs energy. Most of it comes from the sun. Plants are producers. They capture the sun's energy. They use it to grow and reproduce. Any energy that is not used by the plant is stored. Animals are consumers. They eat the plants to get energy for their own life processes. We need energy in order to be able to do anything.
1 Energy is defined as the ability to do work. Every living thing needs energy. Most of it comes from the sun. Plants are producers. They capture the sun's energy. They use it to grow and reproduce. Any energy that is not used by the plant is stored. Animals are consumers. They eat the plants to get energy for their own life processes. We need energy in order to be able to do anything.2 What did you eat this morning? Did you have a bowl of cereal? A piece of toast? These foods are made from grains, which come from plants. When you eat them, you are consuming the energy the plants have stored from the sun. This energy is released by your body. It helps you to do work.
3 Solar energy flows through the food chain. The food chain is a diagram that shows how energy from the sun is used by producers. It also shows how this energy is transferred to consumers in an ecosystem.
4 There is energy all around us. What do we use it for? We use it to keep warm. We use it to power our vehicles. Did you ever stop to think of where this energy comes from? If you heat with wood, it comes from plants. Even fossil fuels such as gasoline come from decayed plants and animals. Where did they get this energy they are now giving off? You guessed it- from the sun!
Assignment= Please copy this graphic organizer into your journal and complete it from the reading above about energy
5 Energy sources are like natural resources. They can be renewable or nonrenewable. Solar energy is, of course, a renewable resource. The sun isn't likely to burn out for billions of years. It will keep sending solar energy our way.
6 Energy from plants is also a renewable energy source. Trees are cut for firewood to heat our homes. They can be replanted. If our forests are managed in this way, we will have wood to use as energy for years to come.
7 Fossil fuels, on the other hand, took millions of years to form. It would take millions of years for them to form again. These are nonrenewable sources of energy. Some examples are coal, oil, and natural gas.
Assignment= Please copy this graphic organizer into your journal and complete it from the reading above about energy
 8 There is a scientific law that says that energy cannot be created or destroyed. However, it can change from one form to another. There are two basic types of energy. Energy is either potential or kinetic.
8 There is a scientific law that says that energy cannot be created or destroyed. However, it can change from one form to another. There are two basic types of energy. Energy is either potential or kinetic.9 Potential energy is stored energy. Think of Niagara Falls. The water at the top of the falls has potential energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. As the water falls over the cliff, the energy changes from potential to kinetic.
Assignment= Please copy this graphic organizer into your journal and complete it from the reading above about energy

10 Gasoline, made from oil, is stored in a tank below the ground. At this point, it has potential energy. When it is burned in a car engine, it makes the car move. It now has kinetic energy.
11 Energy also comes in different "kinds." Some of these include chemical, electrical, mechanical, and nuclear energy. They light our homes. They power our machines and cars. All these different types of energy have one thing in common- they have the ability to do work.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
What Is Energy?
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
What Is Energy?
What Is Energy?
Assignment=Please copy this activity in your journal and complete it there
| What Is Energy? By Patti Hutchison |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Energy is defined as the (1) _______________________ to do work. Every living thing needs energy. Most of it comes from the sun. Plants are producers. They (2) _______________________ the sun's energy. They use it to grow and reproduce. Any energy that is not used by the plant is stored. Animals are consumers. They eat the plants to get energy for their own life processes. We need energy in order to be (3) _______________________ to do anything.
Energy is defined as the (1) _______________________ to do work. Every living thing needs energy. Most of it comes from the sun. Plants are producers. They (2) _______________________ the sun's energy. They use it to grow and reproduce. Any energy that is not used by the plant is stored. Animals are consumers. They eat the plants to get energy for their own life processes. We need energy in order to be (3) _______________________ to do anything.What did you eat this morning? Did you have a bowl of cereal? A piece of toast? These foods are made from grains, (4) _______________________ come from plants. When you eat them, you are consuming the energy the plants have stored from the sun. This energy is released by your body. It helps you to do work.
Solar energy flows through the food chain. The food chain is a (5) _______________________ that shows how energy from the sun is used by producers. It also shows how this energy is transferred to consumers in an (6) _______________________ .
There is energy all around us. What do we use it for? We use it to keep warm. We use it to power our vehicles. Did you ever stop to think of where this energy comes from? If you heat with wood, it comes from plants. Even fossil fuels (7) _______________________ as gasoline come from decayed plants and animals. Where did they get this energy they are now giving off? You guessed it- from the sun!
Energy (8) _______________________ are like natural resources. They can be renewable or nonrenewable. Solar energy is, of course, a renewable resource. The sun isn't likely to burn out for billions of years. It will keep sending solar energy our way.
Energy from plants is also a renewable energy (9) _______________________ . Trees are cut for firewood to heat our homes. They can be (10) _______________________ . If our forests are managed in this way, we will have wood to use as energy for years to come.
Fossil fuels, on the other hand, took millions of years to form. It would take millions of years for them to form again. These are nonrenewable sources of energy. Some examples are coal, oil, and natural gas.
There is a (11) _______________________ law that says that energy cannot be created or destroyed. (12) _______________________ , it can(13) _______________________ from one (14) _______________________ to another. There are two (15) _______________________ types of energy. Energy is either potential or kinetic.
Potential energy is stored energy. Think of Niagara Falls. The water at the top of the falls has potential energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion. As the water falls over the cliff, the energy (16) _______________________ from potential to kinetic.
Gasoline, made from oil, is stored in a tank below the ground. At this point, it has potential energy. When it is burned in a car engine, it makes the car move. It now has kinetic energy.
Energy also comes in different "kinds." Some of these include chemical, electrical, mechanical, and (17) _______________________ energy. They light our homes. They power our machines and cars. All these different types of energy have one thing in common- they have the ability to do work.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
What Is Energy?
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
ASSIGNMENT= Please click the website below and play the game.
Then 1) Explain in your journal exactly what happened. and
2) Explain in your journal why you think it happened in the way it did?
POST TEST
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS |
1. What is an ecosystem? 2. What are the levels of organization within an ecosystem? 3. How do biotic factors differ from abiotic factors? 4. What basic needs are provided by an organism’s habitat? 5. Why do ecologists study both biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem? 6. What is a niche? 7. What factors limit the size of a population? 8. Why do populations’ sizes increase and decrease? 9. How is birth rate related to population size? death rate? 10. How are predator and prey populations related? 11. What are the three major types of interactions among organisms? |




No comments:
Post a Comment