http://www.animate4.com/astronomy/astronomy-space.mpg
Objectives and Indicators For This Unit
2.8. D. Astronomy
1. Identify and describe the components of the universe.
a. Recognize that a galaxy contains billions of stars that cannot be distinguished by the unaided eye because of their great distance from Earth, and that there are billions of galaxies.
b. Identify that our solar system is a component of the Milky Way Galaxy.
c. Identify and describe the various types of galaxies
d. Identify and describe the type, size, and scale, of the Milky Way Galaxy.
2. Identify and explain celestial phenomena using the regular and predictable motion of objects in the solar system.
a. Identify and describe the relationships among the period of revolution of a planet, the length of its solar year, and its distance from the sun.
b. Identify and explain the relationship between the rotation of a planet or moon on its axis and the length of the solar day for that celestial object.
c. Identify and explain the cause of the phases of the moon.
d. Describe how lunar and solar eclipses occur.
e. Identify and describe how the shape and location of the orbits of asteroids and comets affect their periods of revolution.
3. Recognize and explain the effects of the tilt of Earth’s axis.
a. Recognize and describe that Earth's axis is tilted about 23º from vertical with respect to the plane of its orbit and points in the same direction during the year.
b. Recognize and describe that as Earth orbits the sun, the tilt of Earth's axis causes
• Changes in the angle of the sun in the sky during the year
• Seasonal differences in the northern and southern latitudes
c. Recognize and describe how the tilt of Earth's axis affects the climate in Maryland.
4. Recognize and explain how the force of gravity causes the tides.
a. Identify and describe the cause of high and low tides.
Vocabulary Words To be looked up and put in your journal
Rotation
Revolution
Orbit
Day
Night
Year
Seasons
Equinox
Solstice
Galaxy
Universe
Solar System
Star
Nucleus
The Hubble Space Telescope was launched by NASA in 1990. It's a very large telescope! It weighs as much as two elephants. It's as long as a large school bus. It orbits the Earth at about 300 miles per hour, 380 miles above the Earth's surface. 3 The giant telescope was named for astronomer Edwin Hubble. In 1925 Hubble discovered that there were many more galaxies beyond ours. Up until that time, it was thought that our Milky Way Galaxy was the whole universe. Edwin Hubble's work led to the idea that the universe is getting bigger. Galaxies are moving farther apart. This idea led to the Big Bang Theory. It also let scientists guess the age of the universe. They believe the universe is 13 to 14 billion years old.
Why do you
Please answer these questions in your journal from the video.
 1 Our solar system is a small part of a galaxy. Galaxy is the name given to a large system of stars, planets, gas, and dust. Gravity holds a galaxy together. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way galaxy. It has an estimated 200 billion other stars besides our own sun. At least some of these other stars have planets orbiting around them. 2 As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a giant. Its diameter is about 100,000 light years. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. A light year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers or about 6 trillion miles. 3 The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with four arms. This means it is a spiral shape with a bar of bright stars in the center running across the middle. There are four arms that look like they trail off the bar. Our solar system is located in a smaller spiral arm called the Local Group or Orion Arm. 4 Our solar system is about 4.6 billion years old. Our sun is a young star. Scientists think the Milky Way galaxy may be about 14 billion years old.
1 Our solar system is a small part of a galaxy. Galaxy is the name given to a large system of stars, planets, gas, and dust. Gravity holds a galaxy together. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way galaxy. It has an estimated 200 billion other stars besides our own sun. At least some of these other stars have planets orbiting around them. 2 As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a giant. Its diameter is about 100,000 light years. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. A light year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers or about 6 trillion miles. 3 The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with four arms. This means it is a spiral shape with a bar of bright stars in the center running across the middle. There are four arms that look like they trail off the bar. Our solar system is located in a smaller spiral arm called the Local Group or Orion Arm. 4 Our solar system is about 4.6 billion years old. Our sun is a young star. Scientists think the Milky Way galaxy may be about 14 billion years old.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
The Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way Galaxy ASSIGNMENT=Describe a galaxy. (in a short paragraph in your journal)








The Milky Way Galaxy








Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Our solar system is a (1) _______________________ part of a galaxy. Galaxy is the name given to a large system of stars, planets, gas, and (2) _______________________ .(3) _______________________ (4) _______________________ a galaxy (5) _______________________ . Our galaxy is called the Milky Way galaxy. It has an estimated 200(6) _______________________ other stars besides our own sun. At least some of (7) _______________________ (8) _______________________ stars have planets orbiting around them.
Our solar system is a (1) _______________________ part of a galaxy. Galaxy is the name given to a large system of stars, planets, gas, and (2) _______________________ .(3) _______________________ (4) _______________________ a galaxy (5) _______________________ . Our galaxy is called the Milky Way galaxy. It has an estimated 200(6) _______________________ other stars besides our own sun. At least some of (7) _______________________ (8) _______________________ stars have planets orbiting around them.
As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a (9) _______________________ . Its diameter is about 100,000 light years. A light year is the distance that light(10) _______________________ in one year. A light year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers or about 6 trillion miles.
The Milky Way is a (11) _______________________ spiral galaxy (12) _______________________ four arms. (13) _______________________ means it is a (14) _______________________ (15) _______________________ with a bar of bright stars in the center running across the middle. There are four arms that look like they trail off the bar. Our solar system is located in a(16) _______________________ spiral arm called the Local Group or Orion Arm.
Our (17) _______________________ system is about 4.6 billion years old. Our sun is a young star. Scientists think the Milky Way galaxy may be about 14 billion years old.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
The Milky Way Galaxy

PRE-TEST - The Milky Way Galaxy
Phases of the Moon
The Hubble Space Telescope was launched by NASA in 1990. It's a very large telescope! It weighs as much as two elephants. It's as long as a large school bus. It orbits the Earth at about 300 miles per hour, 380 miles above the Earth's surface. 3 The giant telescope was named for astronomer Edwin Hubble. In 1925 Hubble discovered that there were many more galaxies beyond ours. Up until that time, it was thought that our Milky Way Galaxy was the whole universe. Edwin Hubble's work led to the idea that the universe is getting bigger. Galaxies are moving farther apart. This idea led to the Big Bang Theory. It also let scientists guess the age of the universe. They believe the universe is 13 to 14 billion years old.
Why do you
Please watch this video and take between 15-20 notes in your journal
Please answer these questions in your journal from the video.
1. What is "matter"?
2. What do you think are "cosmic individuals"?
3. Who discovered that the universe was as small as a single atom?
4. What do you think the narrator means when he discusses the universe as a "star city"?
5. What do you think it means when experts say that the universe is expanding?
6. What is the "Big Bang Theory"?
7. Why do you think the universe srarted to cool down as it grew larger?
8.
2. What do you think are "cosmic individuals"?
3. Who discovered that the universe was as small as a single atom?
4. What do you think the narrator means when he discusses the universe as a "star city"?
5. What do you think it means when experts say that the universe is expanding?
6. What is the "Big Bang Theory"?
7. Why do you think the universe srarted to cool down as it grew larger?
8.
Astronomy-Universe-Galaxy: Matching
Use the following words:Name: _______________________
| _____ | universe | 1)young hot star |
| _____ | galaxies | 2)group of planets orbiting a star |
| _____ | Milky Way | 3)name of our galaxy |
| _____ | solar system | 4)galaxy with arms coming from the center like pinwheel |
| _____ | yellow | 5)middle-aged star-our sun |
| _____ | blue | 6)flat round or oval galaxy |
| _____ | red | 7)a dying star that explodes |
| _____ | elliptical | 8)186 |
| _____ | spiral | 9)galaxy with no regular shape |
| _____ | irregular | 10)groups of stars |
| _____ | supernova | 11)old cooler star |
| _____ | light year | 12)the stars, galaxies, dust and everything in space |
| The Milky Way Galaxy By Cindy Grigg |  |
 1 Our solar system is a small part of a galaxy. Galaxy is the name given to a large system of stars, planets, gas, and dust. Gravity holds a galaxy together. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way galaxy. It has an estimated 200 billion other stars besides our own sun. At least some of these other stars have planets orbiting around them. 2 As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a giant. Its diameter is about 100,000 light years. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. A light year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers or about 6 trillion miles. 3 The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with four arms. This means it is a spiral shape with a bar of bright stars in the center running across the middle. There are four arms that look like they trail off the bar. Our solar system is located in a smaller spiral arm called the Local Group or Orion Arm. 4 Our solar system is about 4.6 billion years old. Our sun is a young star. Scientists think the Milky Way galaxy may be about 14 billion years old.
1 Our solar system is a small part of a galaxy. Galaxy is the name given to a large system of stars, planets, gas, and dust. Gravity holds a galaxy together. Our galaxy is called the Milky Way galaxy. It has an estimated 200 billion other stars besides our own sun. At least some of these other stars have planets orbiting around them. 2 As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a giant. Its diameter is about 100,000 light years. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. A light year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers or about 6 trillion miles. 3 The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with four arms. This means it is a spiral shape with a bar of bright stars in the center running across the middle. There are four arms that look like they trail off the bar. Our solar system is located in a smaller spiral arm called the Local Group or Orion Arm. 4 Our solar system is about 4.6 billion years old. Our sun is a young star. Scientists think the Milky Way galaxy may be about 14 billion years old.Copyright © 2011 edHelper
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
| _ |
| The Milky Way Galaxy By Cindy Grigg |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Our solar system is a (1) _______________________ part of a galaxy. Galaxy is the name given to a large system of stars, planets, gas, and (2) _______________________ .(3) _______________________ (4) _______________________ a galaxy (5) _______________________ . Our galaxy is called the Milky Way galaxy. It has an estimated 200(6) _______________________ other stars besides our own sun. At least some of (7) _______________________ (8) _______________________ stars have planets orbiting around them.
Our solar system is a (1) _______________________ part of a galaxy. Galaxy is the name given to a large system of stars, planets, gas, and (2) _______________________ .(3) _______________________ (4) _______________________ a galaxy (5) _______________________ . Our galaxy is called the Milky Way galaxy. It has an estimated 200(6) _______________________ other stars besides our own sun. At least some of (7) _______________________ (8) _______________________ stars have planets orbiting around them.As a galaxy, the Milky Way is actually a (9) _______________________ . Its diameter is about 100,000 light years. A light year is the distance that light(10) _______________________ in one year. A light year is about 9.5 trillion kilometers or about 6 trillion miles.
The Milky Way is a (11) _______________________ spiral galaxy (12) _______________________ four arms. (13) _______________________ means it is a (14) _______________________ (15) _______________________ with a bar of bright stars in the center running across the middle. There are four arms that look like they trail off the bar. Our solar system is located in a(16) _______________________ spiral arm called the Local Group or Orion Arm.
Our (17) _______________________ system is about 4.6 billion years old. Our sun is a young star. Scientists think the Milky Way galaxy may be about 14 billion years old.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
 | (Key 1 - Answer ID # 0105645) |
of Syllables | into Syllables |
| 1. |
| |||||
| 2. |
| |||||
| 3. |
| |||||
| 4. |
| |||||
| 5. |
| |||||
| 6. |
| |||||
| 7. |
| |||||
| 8. |
| |||||
| 9. |
| |||||
| 10. |
| |||||
| 11. |
| |||||
| 12. |
| |||||
| 13. |
|
The PlanetsThe nine planets that orbit the sun are (in order from the Sun): Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter (the biggest planet in our Solar System), Saturn (with large, orbiting rings), Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto (a dwarf planet or plutoid). A belt of asteroids (minor planets made of rock and metal) orbits between Mars and Jupiter. These objects all orbit the sun in roughly circular orbits that lie in the same plane, the ecliptic (Pluto is an exception; this dwarf planet has an elliptical orbit tilted over 17° from the ecliptic).
The inner planets (those planets that orbit close to the Sun) are quite different from the outer planets (those planets that orbit far from the Sun).

Small Bodies
There are other smaller object that orbit the Sun, including asteroids, comets, meteoroids and dwarf planets.
The Milky Way Galaxy
 Our solar system is located in the outer reaches of the Milky Way Galaxy, which is a spiral galaxy. The Milky Way Galaxy contains roughly 200 billion stars. Most of these stars are not visible from Earth. Almost everything that we can see in the sky belongs to the Milky Way Galaxy.
Our solar system is located in the outer reaches of the Milky Way Galaxy, which is a spiral galaxy. The Milky Way Galaxy contains roughly 200 billion stars. Most of these stars are not visible from Earth. Almost everything that we can see in the sky belongs to the Milky Way Galaxy.
 The sun is about 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, which is about 80,000 to 120,000 light-years across (and less than 7,000 light-years thick). We are located on on one of its spiral arms, out towards the edge. It takes the sun (and our solar system) roughly 200-250 million years to orbit once around the Milky Way. In this orbit, we (and the rest of the Solar System) are traveling at a velocity of about 155 miles/sec (250 km/sec).
The sun is about 26,000 light-years from the center of the Milky Way Galaxy, which is about 80,000 to 120,000 light-years across (and less than 7,000 light-years thick). We are located on on one of its spiral arms, out towards the edge. It takes the sun (and our solar system) roughly 200-250 million years to orbit once around the Milky Way. In this orbit, we (and the rest of the Solar System) are traveling at a velocity of about 155 miles/sec (250 km/sec).
To reach the center of the Milky Way Galaxy starting from the Earth, aim toward the constellation Sagittarius. If you were in a spacecraft, during the trip you would pass the stars in Sagittarius one by one (and many other stars!).
The Milky way Galaxy is just one galaxy in a group of galaxies called the Local Group. Within the Local Group, the Milky Way Galaxy is moving about 300 km/sec (towards the constellation Virgo). The Milky Way Galaxy is moving in concert with the other galaxies in the Local Group (the Local Group is defined as those nearby galaxies that are moving in concert with each other, independent of the "Hubble flow" expansion).
The inner planets (those planets that orbit close to the Sun) are quite different from the outer planets (those planets that orbit far from the Sun).
- The inner planets are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. They are relatively small, composed mostly of rock, and have few or no moons.
- The outer planets include: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. They are mostly huge, mostly gaseous, ringed, and have many moons (plus Pluto, which is a dwarf planet that has one large moon and two small moons).
Small Bodies
There are other smaller object that orbit the Sun, including asteroids, comets, meteoroids and dwarf planets.
- Asteroids (also called minor planets) are rocky or metallic objects, most of which orbit the Sun in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- Comets are small, icy bodies that orbit the sun. They have very long tails.
- Meteoroids are small bodies that travel through space. They are stony and/or metallic and are smaller than asteroids. Most are very tiny.
The Milky Way Galaxy
From the Earth, our Milky Way Galaxy is visible as a milky band that stretches across the night sky. It is easier to see when you are far from bright city lights. |
To reach the center of the Milky Way Galaxy starting from the Earth, aim toward the constellation Sagittarius. If you were in a spacecraft, during the trip you would pass the stars in Sagittarius one by one (and many other stars!).
The Milky way Galaxy is just one galaxy in a group of galaxies called the Local Group. Within the Local Group, the Milky Way Galaxy is moving about 300 km/sec (towards the constellation Virgo). The Milky Way Galaxy is moving in concert with the other galaxies in the Local Group (the Local Group is defined as those nearby galaxies that are moving in concert with each other, independent of the "Hubble flow" expansion).
The Earth The Earth is round, like a ball, but it is also slightly squashed. We say that its shape is roughly spherical. The Earth travels around the Sun once every year. The Earth also spins on its own axis. The axis is an imaginary line through the centre of the Earth from the North Pole to the South Pole. The Earth spins round once every 24 hours. This causes day and night on Earth. It is day on the part of the Earth that is facing the Sun. It is night on the part of the Earth that is facing away from the Sun.
Please take part in this activity below that compares the planets Mercury and the Earth
http://www.sciencenetlinks.com/interactives/messenger/pits/PlacesInSun.html
Complete a Venn Diagram in your journal about what you learned about the comparison
Please take part in this activity below below that studies the planet Mercury's orbit around the Sun
http://www.sciencenetlinks.com/interactives/messenger/or/OrbitRotation.html
Explain in your journal@ what you learned about Mercury's orbit (2-4 sentences)
Please look at a comparison between the size of the 2 planets - Check out and compare at least 4 pairs of planets
http://www.sciencenetlinks.com/interactives/messenger/psc/PlanetSize.html
Then explain what you learned about the pairs in your journal

Please take part in this activity below that compares the planets Mercury and the Earth
http://www.sciencenetlinks.com/interactives/messenger/pits/PlacesInSun.html
Complete a Venn Diagram in your journal about what you learned about the comparison
Please take part in this activity below below that studies the planet Mercury's orbit around the Sun
http://www.sciencenetlinks.com/interactives/messenger/or/OrbitRotation.html
Explain in your journal@ what you learned about Mercury's orbit (2-4 sentences)
Please look at a comparison between the size of the 2 planets - Check out and compare at least 4 pairs of planets
http://www.sciencenetlinks.com/interactives/messenger/psc/PlanetSize.html
Then explain what you learned about the pairs in your journal
The Moon

The Moon is roughly spherical, but it is a lotsmaller than the Earth.
The Moon travels around the Earth. It goes round once every 28 days.
We only see the part of the Moon that is lit by the Sun. So sometimes we see the whole Moon and sometimes we only see part of the Moon.
The Sun

The Sun is a star and gives out heat and light.
It is roughly spherical in shape and is much, much bigger than the Earth.
The planets
The Earth is just one of eight planets that travel around the Sun. The other planets are called Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
Earth, Sun and Moon
Print
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
PRE - TEST
| The Hubble Space Telescope By Cindy Grigg |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Telescopes let us look at the stars and planets. Telescopes on Earth must be located where there are few city lights. The air must be as clean and(1) _______________________ as possible. Still, waves of light change as they (2) _______________________ (3) _______________________ Earth's(4) _______________________ . This changes the way things look through a telescope on Earth. To solve this (5) _______________________ , a telescope was launched into space.
Telescopes let us look at the stars and planets. Telescopes on Earth must be located where there are few city lights. The air must be as clean and(1) _______________________ as possible. Still, waves of light change as they (2) _______________________ (3) _______________________ Earth's(4) _______________________ . This changes the way things look through a telescope on Earth. To solve this (5) _______________________ , a telescope was launched into space.The Hubble Space Telescope was (6) _______________________ by NASA in 1990. It's a very large telescope! It weighs as much as two elephants. It's as long as a large school bus. It orbits the Earth at about 300 miles per hour, 380 miles (7) _______________________ the Earth's surface.
The giant telescope was named for (8) _______________________ Edwin Hubble. In 1925 Hubble discovered that there were many more galaxies beyond ours. Up until that time, it was thought that our Milky Way Galaxy was the whole universe. Edwin Hubble's work led to the (9) _______________________ that the(10) _______________________ is getting bigger. Galaxies are moving farther (11) _______________________ . This idea led to the Big Bang Theory. It also let scientists guess the age of the universe. They believe the universe is 13 to 14 billion years old.
The Hubble Space Telescope takes pictures of planets, stars, and other galaxies. With Hubble, astronomers have seen the birth and (12) _______________________ of stars. Hubble has taken pictures of galaxies that are billions of light years from Earth. Hubble has showed scientists evidence of black holes. It (13) _______________________ helped to discover dark energy. This strange (14) _______________________ seems to make the universe expand at a faster rate as time goes on. The Hubble Space Telescope gives (15) _______________________ eyes in the sky. With Hubble, astronomers can see farther and more(16) _______________________ than they could see using a telescope on Earth. Who knows what new things may be discovered with the help of the Hubble!
| Phases of the Moon By Patti Hutchison |  |
 1 Was there a full moon last night? Some people believe that a full moon affects people's behavior. Whether that is true or not, the moon does go through phases. What causes the moon to appear differently throughout the month?
1 Was there a full moon last night? Some people believe that a full moon affects people's behavior. Whether that is true or not, the moon does go through phases. What causes the moon to appear differently throughout the month?2 You know that the moon does not give off its own light. When we see the moon shining at night, we are actually seeing a reflection of the Sun's light. The part of the moon that we see shining (lunar phase) depends on the positions of the sun, moon, and the earth.
3 When the moon is between the earth and the sun, we can't see it. The sunlit side of the moon is facing away from us. The dark side is facing toward us. This phase is called the new moon.
4 As the moon moves along its orbit, the amount of reflected light we see increases. This is called waxing. At first, there is a waxing crescent. The moon looks like a fingernail in the sky. We only see a slice of it.
5 When it looks like half the moon is lighted, it is called the first quarter. Sounds confusing, doesn't it? The quarter moon doesn't refer to the shape of the moon. It is a point of time in the lunar month. There are four main phases to the lunar cycle. Four parts- four quarters. For each of these four phases, the moon has orbited one quarter of the way around the earth. This is why it is called a quarter moon when it really looks like a half moon.
6 As the orbit continues, we begin to see more than half of the lighted side of the moon. This is called a waxing gibbous moon. As the lunar month goes on, the moon continues on its path. It comes to a position where the earth is between it and the sun. This time the sunlit side is facing us. We call it a full moon.
7 Once the full moon is reached, we start to see less and less of the sunlit side. It looks like tiny slices are being taken off. This is called waning. When we still see more than half the moon shining, it is called a waning gibbous moon.
8 Soon, the moon reaches its third quarter phase. Again, it looks like only half the moon is lighted. We are seeing half the sunlit side. As we begin to see less and less of the sunlit portion, the moon is becoming a waning crescent. Soon it will "disappear" once again and become a new moon.
9 There are four lunar phases: new moon, first quarter, full moon, and last quarter. It takes the moon about 29.5 days to complete this cycle. This is called a lunar month. Ancient civilizations set their calendars by the phases of the moon. Many calendars, and even some clocks, keep track of the moon's phases yet today.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
| Name _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
| Name _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| Phases of the Moon By Patti Hutchison |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Was there a full moon last night? Some people believe that a full moon affects people's (1) _______________________ . Whether that is true or not, the moon does go through phases. What causes the moon to (2) _______________________ differently (3) _______________________ the month?
Was there a full moon last night? Some people believe that a full moon affects people's (1) _______________________ . Whether that is true or not, the moon does go through phases. What causes the moon to (2) _______________________ differently (3) _______________________ the month?You know that the moon does not give off its own light. When we see the moon shining at night, we are actually seeing a reflection of the Sun's light. The part of the moon that we see shining (lunar phase) depends on the (4) _______________________ of the sun, moon, and the earth.
When the moon is between the earth and the sun, we can't see it. The sunlit side of the moon is facing away from us. The dark side is facing toward us. This phase is called the new moon.
As the moon moves (5) _______________________ its orbit, the amount of reflected light we see increases. This is called waxing. At first, there is a waxing crescent. The moon looks like a fingernail in the sky. We only see a slice of it.
When it looks like half the moon is lighted, it is called the first quarter. Sounds confusing, doesn't it? The quarter moon doesn't refer to the (6) _______________________ of the moon. It is a (7) _______________________ of time in the lunar month. There are four main phases to the lunar cycle. Four parts- four quarters. For each of these four phases, the moon has orbited one quarter of the way around the earth. This is why it is called a quarter moon when it really looks like a half moon.
As the orbit continues, we begin to see more than half of the lighted side of the moon. This is called a (8) _______________________ (9) _______________________ moon. As the lunar month goes on, the moon continues on its path. It comes to a (10) _______________________ where the earth is between it and the sun. This time the sunlit side is facing us. We call it a full moon.
Once the full moon is reached, we start to see less and less of the (11) _______________________ side. It looks like tiny slices are being taken off. This is called waning. When we still see more than half the moon shining, it is called a waning gibbous moon.
Soon, the moon reaches its (12) _______________________ quarter phase. Again, it looks like only half the moon is lighted. We are seeing half the sunlit side. As we begin to see less and less of the sunlit (13) _______________________ , the moon is (14) _______________________ a waning crescent. Soon it will "disappear" once again and (15) _______________________ a new moon.
There are four lunar phases: new moon, first quarter, full moon, and last quarter. It takes the moon about 29.5 days to (16) _______________________ this cycle. This is called a lunar month. Ancient civilizations set their calendars by the phases of the moon. Many calendars, and even some (17) _______________________ , keep track of the moon's phases yet today.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
| Name _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
| Eclipses By Patti Hutchison |  |
 1 The sky begins to grow dark, yet it is noon. The sun appears to have a little bite taken out of it. What is going on? You are experiencing a solar eclipse.
1 The sky begins to grow dark, yet it is noon. The sun appears to have a little bite taken out of it. What is going on? You are experiencing a solar eclipse.2 The full moon was bright in the night sky. All of a sudden, a corner appears to be carved out of it. A lunar eclipse is about to take place.
3 Both the sun and the moon experience eclipses. An eclipse happens when the light is blocked. There are both partial and total eclipses. What causes these awesome events?
4 A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes directly between the sun and the earth. The moon actually blocks our view of the sun. How can this be, when the sun is much larger than the moon? Remember that the sun is much farther away from the earth than the moon is. This causes them to appear to be about the same size as we look at them in the sky.
5 As a total solar eclipse takes place, we see less and less of the sun. Soon, the moon totally blocks the disk shape of the sun. We see only the sun's gaseous outer layers. The middle is perfectly black. As the moon continues to move, more of the sun begins to appear. A solar eclipse looks similar to the phases of the moon. But the "phases" happen much quicker!
6 Only a small portion of the earth will see the total eclipse. This is because the moon casts a shadow on the earth. This shadow has two regions, the umbra and the penumbra.
7 The umbra is the inner portion of the shadow. It does not receive direct sunlight. People who are watching from the umbra see a total solar eclipse. The penumbra does receive some sunlight. This is a wider area. People watching from the penumbra only see a partial eclipse.
8 You should never look directly at the sun. The rays can do great damage to your eyes. Therefore, you can't watch an eclipse without special filters for your eyes. There are several ways to watch this awesome event safely, however. There are special glasses you can buy. Sunglasses DO NOT work. You can also make your own pinhole projector or viewer. You can find information about how to protect your eyes from permanent damage online or at the library.
9 Solar eclipses, especially total ones, happen very rarely. Lunar eclipses happen a little more often. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes through the earth's shadow. This happens only when there is a full moon. The earth is between the moon and the sun, blocking the reflected light. The moon turns dark.
10 The shadow of the earth also has an umbra and a penumbra. When the whole moon is inside the earth's umbra, a total eclipse occurs. The moon can still be seen, although it has a reddish color. This is caused by the bending of sunlight by the earth's atmosphere.
11 Eclipses don't happen every month, even though the sun, moon, and earth may be in the right alignment. This is because the orbits pass above or below the perfect positions that would cause an eclipse. The maximum number of eclipses that can be seen in one year is seven. This occurred in 1982, but it won't happen again until 2038!
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
| Name _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
| Eclipses By Patti Hutchison |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 The sky begins to grow dark, yet it is noon. The sun appears to have a little bite taken out of it. What is going on? You are experiencing a solar(1) _______________________ .
The sky begins to grow dark, yet it is noon. The sun appears to have a little bite taken out of it. What is going on? You are experiencing a solar(1) _______________________ .The full moon was bright in the night sky. All of a sudden, a corner appears to be carved out of it. A lunar eclipse is about to take place.
Both the sun and the moon experience (2) _______________________ . An eclipse happens when the light is blocked. There are both partial and total eclipses. What causes these awesome events?
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes directly between the sun and the earth. The moon actually blocks our view of the sun. How can this be, when the sun is much larger than the moon? Remember that the sun is much farther away from the earth than the moon is. This causes them to appear to be about the same size as we look at them in the sky.
As a total solar eclipse takes place, we see less and less of the sun. Soon, the moon (3) _______________________ blocks the disk shape of the sun. We see only the sun's (4) _______________________ outer layers. The middle is perfectly black. As the moon continues to move, more of the sun begins to appear. A solar eclipse looks similar to the phases of the moon. But the "phases" happen much quicker!
Only a small portion of the earth will see the total eclipse. This is because the moon casts a shadow on the earth. This shadow has two regions, the umbra and the penumbra.
The umbra is the inner (5) _______________________ of the shadow. It does not (6) _______________________ (7) _______________________ sunlight. People who are watching from the umbra see a total solar eclipse. The (8) _______________________ does receive some sunlight. This is a wider area. People watching from the penumbra only see a partial eclipse.
You should never look directly at the sun. The rays can do great damage to your eyes. Therefore, you can't watch an eclipse without special filters for your eyes. There are (9) _______________________ ways to watch this awesome event safely, however. There are special glasses you can buy. (10) _______________________ DO NOT work. You can also make your own (11) _______________________ projector or viewer. You can find information about how to protect your eyes from permanent damage (12) _______________________ or at the library.
Solar eclipses, especially total ones, happen very rarely. Lunar eclipses happen a little more often. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon passes through the earth's shadow. This happens only when there is a full moon. The earth is between the moon and the sun, blocking the reflected light. The moon turns dark.
The shadow of the earth also has an (13) _______________________ and a penumbra. When the whole moon is inside the earth's umbra, a total eclipse occurs. The moon can still be seen, although it has a reddish color. This is caused by the bending of sunlight by the earth's (14) _______________________ .
Eclipses don't happen every month, even though the sun, moon, and earth may be in the right (15) _______________________ . This is because the orbits pass above or below the perfect positions that would cause an eclipse. The (16) _______________________ number of eclipses that can be seen in one year is seven. This occurred in 1982, but it won't happen again until 2038!
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Standard 2.0 Earth/Space Science |
Topic D. Astronomy |
Indicator 1. Recognize that objects of our solar system are interrelated. |
Objective c. |
Selected Response Item | |
|---|---|
The solar system containing Earth consists of a sun and planets. Which statement best describes the motion of the planets in our solar system?
/toolkit/vsc/assessment_items/msa_science_6_026.xml | Correct Answer: C |
Public Release #1 - Selected Response (SR) Item
Science Grade 5 Objective 2.D.1.b
The sun appears to rise in the east and set in the west each day. During the day, the sun is
as planets and stars, are often visible
The data table below contains information about the planets in our solar system.
Which of these changes on Earth would be likely if Earth were farther from the sun?
A. lower temperatures
B. higher temperatures
C. more hours in the day
D. fewer days in the year
Science Toolkit: Grade 5 Objective 2.D.1.b
Content from http://mdk12.org/instruction/curriculum/science/standard2/grade5.html 3
Public Release #2 - Selected Response (SR) Item
Science Grade 5 Objective 2.D.1.b
The data table below compares four characteristics of the inner planets.
Planets
Mercury Venus Earth Mars
Temperature -184°C to 527°C -450°C to 477°C -89°C to 58°C -143°C to 17°C
Mass (kilograms) 3.30 × 102 3 4.87 × 102 4 5.97 × 102 4 6.42 × 102 3
Diameter
(kilometers)
4,854 12,112 12,751 6,788
Distance from sun
(millions of
kilometers)
58 108 150 228
Which of these statements best explains why Earth is the only inner planet that supports
life?
A. The other planets have too much mass.
B. The other planets are too close to the sun.
C. The other planets are either too hot or too cold.
D. The other planets are either too big or too small.
Science Toolkit: Grade 5 Objective 2.D.1.b
Content from http://mdk12.org/instruction/curriculum/science/standard2/grade5.html 4
Characteristic
so bright that other objects in space are rarely visible. At night, other objects in space, such
POST TEST
· How do scientists think the universe began? |
· Are all of the galaxies in the universe the same?
· What is the Milky Way Galaxy?
· What is rotation? Revolution?
· Why is the length of year on Earth different from the length of year in other planets?
· Why is the length of day on Earth different from the length of day in other planets?
· Why does it appear to an observer on Earth that the sun rises in the east and sets in the west?
· Why does the shadow of a still object move during the day?
· What causes the regular cycle of different seasons on Earth?
· Why is the length of daylight generally longer during summer and shorter during winter?
· Why does the northern hemisphere experience summer while the southern hemisphere experiences winter from June 21 to September 20 every year?
· Why does the northern hemisphere experience winter while the southern hemisphere experiences summer from December 21 to March 20 every year?
· Why is the length of day equal to the length of night during vernal and autumnal equinox?
· What makes the moon visible when it does not produce light?
· Why does the moon's appearance change throughout the month as observed from Earth? What are phases?
· What causes tides?
List three things that you have learned about the North and South Poles from this lesson. Which one was most interesting for you to learn? Explain why. (In your JOURNAL)

| The Reason for the Seasons By Brandi Waters |  |
| copy |
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
ASSIGNMENT=Please
The Reason for the Seasons
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
| Name _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ (Key 1 - Answer ID # 0622993) |
Write each word three times.
| equinox |
| certain |
| solar |
| consider |
| rise |
| rotation |
| autumnal |
| reason |
| longer |
| during |
| astronomy |
| throughout |
| whether |
| latitude |
| opposite |
copy into your journal and answer the questions there |
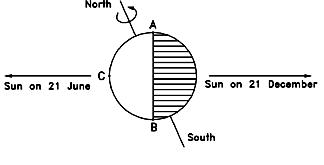 If you are like most people living on Earth, you experience four different seasons throughout the year. What each season means to you depends on where you live. To you, winter might mean building snowmen or going ice skating. It could also mean temperatures around sixty degrees. Spring may mean sunshine and melting snow. It might also mean clouds and thunderstorms. For many, summer begins in the month of June. (1) _______________________ , in some parts of the world, summer begins in December!
If you are like most people living on Earth, you experience four different seasons throughout the year. What each season means to you depends on where you live. To you, winter might mean building snowmen or going ice skating. It could also mean temperatures around sixty degrees. Spring may mean sunshine and melting snow. It might also mean clouds and thunderstorms. For many, summer begins in the month of June. (1) _______________________ , in some parts of the world, summer begins in December!Why do we have four seasons here on Earth? Why do the four seasons mean different things in different parts of the world? There is more to understanding the seasons than you might think. You need to know about (2) _______________________ and geography. To really understand the seasons, you have to look at Earth from space. You need to understand how the Earth is arranged in space, how it spins, and how it orbits around the sun. All of these things are important in understanding why Earth has four seasons. If you look at the Earth from space, you will see that it is tilted. Earth's axis is not vertical. The North Pole is not at the top of the Earth. The Earth's axis is tilted approximately 23.5 degrees. This tilt is what creates the four seasons. As the Earth moves around the sun during the year, the direction in which the axis is pointing changes. Sometimes the North Pole is tilted toward the sun. Sometimes it is tilted away from the sun.
The equator is an imaginary line that divides the Earth into northern and southern hemispheres. Each hemisphere has (3) _______________________ seasons. When the North Pole is tilted toward the sun, the South Pole is tilted away from the sun. In July, it is summer in the northern hemisphere. In the southern hemisphere, it is winter! Summer and winter happen at the same time! They just happen in different parts of the world.
As the Earth moves around the sun, it also spins on its axis. Earth's axis is an invisible line that runs through the Earth from the North Pole to the South Pole. The Earth spins on its axis to give us day and night. It takes twenty-four hours for the Earth to make a full rotation. Earth's spinning is what makes the sun (4) _______________________ to rise and set each day. Even though it (5) _______________________ to be the sun that is moving each day, it is really the Earth that is moving. As the Earth spins, each place on Earth faces a different direction in space. For part of the day, each place on Earth faces the sun. During the rest of the day, each place faces away from the sun and toward the edge of the (6) _______________________ system. This part of each day is night. This happens everywhere on Earth, except for the poles. The poles are on the Earth's axis. They do not face a new direction as the Earth spins. This means that the sun does not rise and set each day at the poles. Instead, the sun rises and sets with the seasons. The poles only face different directions in space as the Earth orbits around the sun. At the poles, there is one sunrise and one sunset each year! They (7) _______________________ at the time of the spring and autumnal equinoxes. An equinox(8) _______________________ when the Earth's axis neither points toward the sun nor away from it. On an equinox, the poles lie on the border where night changes to day. The sun rises on the spring equinox and shines all summer long. It sets on the (9) _______________________ equinox during the fall. Winter is like a very long night. There is no sun.
Summer means warmer weather and longer days in most places on Earth. The amount of daylight in a day varies a lot. It all depends on where you are. Near the equator, the days are about the same length year round. Each day is about twelve hours long. The days last a few minutes (10) _______________________ during the summer and are a few minutes shorter during the winter. As you move from the equator toward the poles, the days during the summer become longer. The days during the winter (11) _______________________ shorter. A summer day in Hawaii is about thirteen hours long, while a summer day in Alaska could be twenty hours long! With all of that sunlight, why is it so cold in Alaska?
The weather near the equator is warm. The weather near the poles is cold. This is because of the way the sun heats the Earth. The sun's energy is made up of light and heat. It moves from the sun to Earth in a direct path. Most of the sun's energy hits the Earth near the equator. The poles only get a small amount of the sun's energy, and never a direct hit. It isn't enough energy to melt the ice and warm the oceans and land, even in the summer. This is why places near the equator are warmer than places near the poles.
There is one more thing to (12) _______________________ regarding temperatures and weather patterns on Earth. Two different places on Earth with the same (13) _______________________ often have very different temperatures and weather patterns. Most often, this is because the two places are at different (14) _______________________ . Altitude is the distance a place is from sea level. A city near sea level is much warmer than a city in the mountains. (15) _______________________ can make the difference between (16) _______________________ a city has a cold, rainy winter or a cold, snowy winter.
There is a lot to know to understand why the Earth's four seasons happen and why they are so different all over the world. A lot of things work together to (17) _______________________ how you(18) _______________________ each season in the place where you live. One thing you can know for certain though: the tilt of the Earth is the reason for the seas

No comments:
Post a Comment