1.6-8.A Constructing Knowledge 1. Design, analyze or carry out simple investigations and formulate appropriate conclusions based on the data obtained or provided. 1.6-8.B. Applying Evidence and Reasoning 1. Review data from a simple experiment, summarize the data, and construct a logical argument about the cause-and-effect relationships in the experiment. 1.6-8.C Communicating Scientific Information 1. Develop explanations that explicitly link data from investigations conducted, selected readings and when appropriate, contributions from historical discoveries. 1. Analyze the value and the limitations of different types of models in explaining real things and processes.
|
· Organisms possess structures and behaviors, which indicate their relatedness. | |
| |
· Living things grow, use food, reproduce, and respond to their surroundings. · Biologists use a classification system to organize living things into groups by shared characteristics. · Animals and plants can be grouped by observable features and can be placed in different groups. · Some organisms consist of only a single cell, while others are multicellular. · Living things are made of cells. · Cells vary greatly in appearance and perform very different roles in the organism · Some organisms have characteristics that make them better suited to certain environments. 1st BIG assignment = Please look up these vocabulary words and put the words and their definitions into your journal.
PRETEST- Please copy in your journal, date it, and
· What are the characteristics of living things? · How are living things classified? |
· What are the distinguishing characteristics of bacteria? |
· What are the characteristics of protists? How do protists differ? |
· What are the defining characteristics of fungi? |
· What are the defining characteristics of plants? How do plant groups differ?
· What are the defining characteristics of animals? What are the main characteristics of the following groups of animals: sponges, cnidarians, worms, mollusks, echinoderms, arthropods? |
What are the major groups of vertebrates and how do they differ?
Please copy in your journal, date it, and |
|
|
Complete each sentence using the words in the word list.
lifespan" | Reproduce | Lifespan |
|
|
Metabolism | Response | Growth |
|
|
|
_______________ | 1. | We made graphs to show the plants' ____. |
_______________ | 2. | Most bacteria ____ by binary fission. |
_______________ | 3. | The ____ of the mercantile industry, or trading industry, led to the economic success of the U.S. colonies. |
_______________ | 4. | Individuals with a fast ____ burn calories quickly. |
_______________ | 5. | Jasper's ____ processed Cheez Doodles into energy quickly. |
_______________ | 6. | Do you think not getting enough sleep will stunt your ____? |
_______________ | 7. | A definition of "____; is how long something lives. |
_______________ | 8. | Some organisms have a faster ____ that others. |
_______________ | 9. | Scientists stay that the ____ of a wild sun bear is still unclear. |
_______________ | 10. | The relationship of the rain to the crops affects their ____. |
_______________ | 11. | Not everyone's ____ is the same. |
_______________ | 12. | A stimulus is a change that causes a ____. |
_______________ | 13. | His ____ showed how virtuous he truly. |
_______________ | 14. | Allice's face turned red in ____ to her social gaffe. |
_______________ | 15. | All Muslims should make a pilgrimage to Mecca at some time during their ____. |
_______________ | 16. | Lack of water caused the plants ____ to be stunted. |
|
|
|
Please read this article and answer the questions in your journal There are many different things living on Earth. Living things have a variety of traits and characteristics. Some living things cannot move at all. Other things have wings, fins, or legs. Some are large, and others are quite small. Scientists call all living things organisms. But scientists needed to separate all of these organisms into different groups in order to study them.
Please read this article and answer the questions in your journal |
|
Scientists use classification to learn more about the multitude of organisms on Earth. Scientists put these living things into different groups. These groups are based on the characteristics that the organisms share. The characteristics of one group are different than the characteristics of another group. One example of the way animals are grouped is what they look like. For example, an organism may be covered in feathers or fur. It may have flowers or broad leaves etc. Physical features help scientists to put the organisms in different classifications or groups. Assignment= Context Clues: Please explain in your journal what do you think "multitude" means in the previous paragraph?
Assignment= Context Clues: Please explain in your journal what do you think "physical features" means in the previous paragraph? Assignment= Please copy this question and it's possible answers in your journal and answer this question from the reading. "Why do you think scientists classify horses and zebras in the same group?" a) They eat similar foods. b) They run at similar speeds c) They have similar predators that eat them d) They have similar physical features
Please copy in your journal, date it, and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Complete each sentence.
_______________ | 1. | The classification groups are: kingdom, (phylum, Germination, Lifespan) , class, order, family, genus, and species. |
_______________ | 2. | Animals and some plants (Anus, reproduce, Eubacteria) with sexual reproduction. |
_______________ | 3. | His (Anus, response, Radial Symmetry) to the teacher's question was very interesting. |
_______________ | 4. | (Sponges, Cell Wall, Lifespan) with spicules are not the sponges used for cleaning. |
_______________ | 5. | Fungi grow from (spores, Lifespan, Phylum) in the air. |
_______________ | 6. | Most bacteria (Echinoderms, Gill, reproduce) by binary fission. |
_______________ | 7. | With the help of sunlight and (chlorophyll, Protists, Monera) , the leaf makes glucose. |
_______________ | 8. | there are several (Arthropods, Bilateral Symmetry, species) of bees. |
_______________ | 9. | The basketball player has a large (Vertebrate, Reproduce, lung) capacity. |
_______________ | 10. | A red blood (Mollusks, Kidney, cell) carries oxygen around the body. |
_______________ | 11. | An herbivore is a consumer that eats (Invertebrate, plants, Adaptation) . |
_______________ | 12. | A (Eukaryotes, Lifespan, Fungi) mitochondria evolved from bacteria and its chloroplasts from cyanobacteria. |
_______________ | 13. | Can you (reproduce, Kingdom, asnimals) your lab results. |
|
|
|
Please read this article and answer the questions in your journal |
|
What makes a living thing a plant? All plants have the following characteristics: 1. Plants make their own food. 2. Plants cannot move from place to place. 3. Plant cells have structures called "cell walls". Although all plants share their traits, some plants share more characteristics with one another than with other plants. Scientists separate plants into 2 main groups based on their characteristics. They classify the plant as being vascular or being nonvascular.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying plants |
|
|
|
Vascular plants have leaves, stems and roots. Their roots, stems and leaves contain tubes made up of vascular tissue that carries water and nutrients throughout the plant. These tube are very, very small. But the plants can grow very tall because of these tubes. Bushes, trees, and grass are examples of vascular plants. Nonvascular plants do not have true roots, stems and leaves. They also do not have many vascular tissues. They cannot move water and nutrients great distances, so they are usually smaller plants. Mosses, and liverwort are examples of nonvascular plants.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying 2 kinds of plants |
|
|
|
Please read this article and answer the questions in your journal |
|
What makes an organism an animal? All animals have the following 3 characteristics: 1) Animals cannot make their own food. 2) Animals can move from place to place. 3) Animal cells do not have cell walls. Scientist classify animals into 2 main groups: vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates have a hard, bumpy backbone that holds the body up. Invertebrates do not have a backbone.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying animals |
|
|
|
 There are several main groups of vertebrate animals. They are birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. There are several main groups of vertebrate animals. They are birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
Invertebrate animals include animals such as insects, spiders, snails, crabs, jellyfish, squid and worms.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying 2 kinds of animals |
|
|
|
Assignment= Please explain in your journal how tigers and worms are both animals. Which of these 4 characteristics do they both have? a. They both have cells with cell walls. b. They both make their own food. c. They both have back bones. d. They both can move around. Please click this site below and play the game. Please explain in your journal what you learned from the game in 3-5 sentences.
Please copy in your journal, date it, and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Complete each sentence.
_______________ | 14. | During a bowel movement the rectum pushes waste out through the (anus, Metabolism, Protists) . |
_______________ | 15. | The large (Germination, exoskeleton, Bilateral Symmetry) of the lobster keeps it safe from some predators. |
_______________ | 16. | A person has more than one (phloem, Eukaryotes, lung) . |
_______________ | 17. | The urinary system includes the (Exothermic, Adaptation, kidney) and bladder. |
_______________ | 18. | (Monera, Echinoderms, Cnidarians) have an endoskeleton, or internal skeleton. |
_______________ | 19. | The environment can affect the (growth, Gill, Bilateral Symmetry) and health of living things. |
_______________ | 20. | Mushrooms, molds, and yeast are (Bilateral Symmetry, Xylem, fungi) . |
_______________ | 21. | Eukaryotes have a nucleus, but (Adaptation, prokaryotes, Radial Symmetry) do not. |
_______________ | 22. | One (adaptation, Xylem, Prokaryotes) of frogs is that they have developed webbed feet to help them swim. |
_______________ | 23. | The burning of fossil fuels for (Heterotroph, Kingdom, energy) causes air pollution. |
_______________ | 24. | The thick fur of some animals is an (Fungi, Exothermic, adaptation) to cold environments. |
_______________ | 25. | Plants that have (Gill, vascular, Sponges) tissue are called vascular plants. |
_______________ | 26. | Snails, cowries and clams are (Metabolism, mollusks, Lung) . |
Name _____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Complete each sentence.
_______________ | 27. | The relationship of the rain to the crops affects their (growth, Autotroph, Response) . |
_______________ | 28. | The bodies of two-shelled (Eukaryotes, mollusks, Endothermic) consist of two shells clamped with a large muscle. |
_______________ | 29. | Ferns and mushrooms produce (Archeabacteria, Germination, spores) . |
_______________ | 30. | Homeostasis is a natural (response, Chlorophyll, Growth) by your body to keep your inside temperature the same even when the outside temperature changes. |
_______________ | 31. | The (phloem, cell, Kidney) in the tree allowed the maple syrup to travel to its destination. |
_______________ | 32. | Water is needed for (metabolism, Exoskeleton, Growth) . |
_______________ | 33. | Man is an example of a (vertebrate, Prokaryotes, Spores) animals. |
_______________ | 34. | Plants that have (Energy, Kingdom, vascular) tissue are called vascular plants. |
_______________ | 35. | (Prokaryotes, Arthropods, Endothermic) have a hard exoskeleton rather than an internal skeleton. |
_______________ | 36. | Liverworts and hornworts are (Vertebrate, nonvascular, Protists) plants. |
_______________ | 37. | The biosphere has all the materials living things need to live, grow, and (Adaptation, reproduce, cell) . |
_______________ | 38. | The (lifespan, Monera, Gill) of a hamster is about 2 years. |
_______________ | 39. | (Cell Wall, Plants, Nonvascular) grow best in Tifton soils. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Making New Groups People once thought that everything alive on earth was either a plant or an animal. Over time, scientists gained new knowledge about living things and discovered new organisms. They realized that not all living things fit the characteristics of plants or animals. One such example is that of the mushroom. Mushrooms cannot make their own food, and they cannot move. Since they cannot make their own food, they are not plants. Since they cannot move around, they are not animals. The scientists had to make a new group for them. They are now part of the "fungi" group. The fungus organism is also a part of the same group. Other new groups like bacteria and slime molds also have their own groups that are not connected to plants or animals. The classification of organisms helps scientists determine how related different organisms are to each other. Relatedness is a word scientists use to explain how much or how little two organisms have in common. Living beings in the same group have characteristics in common. They are more closely related to each other than they are to organisms in other groups. Scientists separate different organisms within the same group into smaller groups based on their characteristics. The smaller the group., the more closely related its members are. For example, human beings belong to a group of vertebrate animals called mammals. Some other animals in this group are dolphins, bears, rats, and apes. Another example is with frogs, worms and snails. They are all animals. They are more closely related to each other than they are to ANY plant. Yet, worms and snails are invertebrates, and frogs are vertebrates. This also means that worms and snails are more closely related to each other than they are to frogs. Scientists classify all 3 living things into a large group - animals; however, they classify worms and snails as invertebrates, and frogs as vertebrates.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ relatedness and smaller groups of classifying |
|
|
|
In some situations, plants or animals look very similar when they are not very closely related. For example, birds, bats, and bees all can fly with wings. Yet, bees have no backbones so they are different than the vertebrate birds and bats. The scientists have to take the classification system even further with these 3 flying animals. Birds and bats both are vertebrates, but scientists put them in different groups because they have different characteristics. They are:bats five birth to their young and have fur, and birds lay eggs and have feathers. Vertebrates (birds and bats)
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ relatedness and smaller groups of classifying |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main Idea and Details
Assignment= Please take 3 notes in your journal about each of the 5 different kingdoms of life in the reading below
Five Kingdoms of Lifeby Beth RowenEvery living creature on Earth belongs to a kingdom. Scientists debate how many kingdoms there are, but most agree there are five. Here is how the five kingdoms are organized.
MoneraMonera are single-celled organisms that don’t have a nucleus. Bacteria make up the entire kingdom. There are more forms of bacteria than any other organism on Earth. Some bacteria are beneficial to us, such as the ones found in yogurt. Others can cause us to get sick.
ProtistsProtists are mostly single-celled organisms that have a nucleus. They usually live in water. Some protists move around, while others stay in one place. Examples of protists include some algae, paramecium, and amoeba.
FungiFungi are usually motionless organisms that absorb nutrients for survival. They include mushrooms, molds, and yeasts.
PlantsPlants contain chlorophyll, a green pigment necessary for photosynthesis, a process in which plants convert energy from sunlight into food. Their cell walls are made sturdy by a material called cellulose, and they are fixed in one place. Plants are divided into two groups: flower- and fruit-producing plants and those that don’t produce flowers or fruits. They include garden flowers, agricultural crops, grasses, shrubs, ferns, mosses, and conifers.
AnimalsAnimals are the most complex organisms on Earth. Animals are multi-celled organisms, eat food for survival, and have nervous systems. They are divided into vertebrates and invertebrates and include mammals, amphibians, reptiles, birds and fish.
Please copy in your journal, date it, and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name _____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Complete each sentence.
_______________ | 40. | The sponge is the oldest type of (Anus, Bilateral Symmetry, invertebrate) . |
_______________ | 41. | His (Fungi, response, Transpiration) showed how virtuous he truly. |
_______________ | 42. | All living things can (reproduce, Fungi, Kidney) . |
_______________ | 43. | Worms and humans are both in the (kingdom, Mollusks, Radial Symmetry) Animalia. |
_______________ | 44. | The white spines of the cactus are a form of a protective (Endothermic, adaptation, Kingdom) . |
_______________ | 45. | Ferns reproduce without seeds, by (Reproduce, Germination, spores) . |
_______________ | 46. | Some (Mollusks, Anus, cnidarians) are shaped like a vase which is known as a polyp form. |
_______________ | 47. | A mushroom is an example of a (phloem, Nonvascular, fungi) . |
_______________ | 48. | Most plants are dependent on sunlight for (Protists, growth, cell) . |
_______________ | 49. | A jellyfish is an (cell, invertebrate, Archeabacteria) that shoots poison at its enemies. |
_______________ | 50. | The biologist enjoyed seeing the (Chlorophyll, cell, Cnidarians) at the tidepools. |
_______________ | 51. | Animals, plants, (Radial Symmetry, fungi, Kidney) and microbes have survival needs that need to be met in order to surive. |
_______________ | 52. | (Sponges, Prokaryotes, Endothermic) first appeared on Earth 580 million years ago. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Classifying Animals
| The inventor of modern scientific classification was Carolus Linnaeus (1707-1778) a Swedish botanist who classified and described more than 4,400 species of animals and 7,700 species of plants. |
There are billions of different kinds of living things (or organisms) on earth. To help study them, biologists have devised ways of naming and classifying them according to their similarities and differences.
The system most scientists use puts each living thing into seven groups (ortaxons), organized from most general to most specific. Therefore, each species belongs to a genus, each genus belongs to a family, each family belongs to an order, etc.
From largest to smallest, these groups are:
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Order
- Family
- Genus
- Species
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying animals |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kingdoms are huge groups, encompassing millions of kinds of organisms each. All animals are in one kingdom (called Kingdom Animalia); all plants are in another (Kingdom Plantae). In the most widely-used system, there are five kingdoms, containing animals, plants, fungi, prokaryotes, and protoctists (the last two are different sorts of one-celled organisms). Other systems have six or more kingdoms.
Species are the smallest groups. A species consists of all the animals of the same type, who are able to breed and produce young of the same kind. For example, while any two great white sharks are in the same species, as are any two makos, great whites and makos are in different species (since they can't interbreed).
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ kingdoms |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main Idea and Details
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ species |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A Sample ClassificationThe lion belongs to the following groups:
- Kingdom Animalia (includes all animals)
- Phylum Chordata (includes all vertebrate animals, as well as some other more primitive ones)
- Class Mammalia (includes all mammals)
- Order Carnivora (includes carnivorous mammals, from bears to raccoons to harbor seals)
- Family Felidae (includes all cats)
- Genus Panthera (includes the great roaring cats: lions, tigers, jaguars, and leopards)
- Species leo (lions!)
For more, see Examples of Scientific Classification
Fact Monster/Information Please® Database, © 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
Six Kingdoms
By Cindy Grigg | |  |
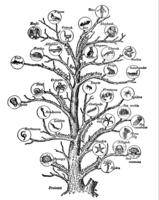 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek scholar Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these large groups into smaller groups called subgroups. For example, plants were divided into trees, shrubs, or herbs. Animals were classified by how they moved. Animals that could fly were put into one subgroup. Animals that could swim were in another subgroup. Animals that walked, crawled, or ran were lumped into another subgroup. 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek scholar Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these large groups into smaller groups called subgroups. For example, plants were divided into trees, shrubs, or herbs. Animals were classified by how they moved. Animals that could fly were put into one subgroup. Animals that could swim were in another subgroup. Animals that walked, crawled, or ran were lumped into another subgroup.
2 Nearly two thousand years later, the Swedish biologist Carolus Linnaeus created a different classification system. His idea was to group animals and plants based on similarities in their structures. For example, Linnaeus placed animals into groups based on whether or not they had a backbone. Like Aristotle, Linnaeus divided living things into two large groups - plants or animals. He called these groups "kingdoms." But today's scientists have tools and technology available to them that have allowed them to study organisms more closely. Scientists now realize that some organisms don't quite fit into the plant or animal group. As a result, several other kingdoms of organisms are now used. Today's scientists look at cell structure, how the organism moves, gets food, and reproduces.
3 This is an explanation of the six kingdom classification system. First is the animal kingdom. Members of the animal kingdom are made up of many cells. Their cells have a nucleus that is contained inside a membrane. All animals get their food by eating other organisms. Animals are divided into two large subgroups: invertebrates (those without backbones) and vertebrates (those with backbones). Examples of vertebrates are fish, frogs, lizards, eagles, dogs, and people. Invertebrate animals include sponges, jelly fish, coral, insects, worms, and sea stars.
4 The plant kingdom's members are made of many cells that have an outer cell wall. They also have a membrane-bound nucleus. All plants make their own food by photosynthesis. Some groups of plants are ferns, mosses, conifers, and flowering plants. Mosses and ferns reproduce by spores. Conifers make seeds in cones. Flowering plants make seeds in their flowers. Some examples of plants are maple trees, pine trees, ferns, dandelions, moss, roses, and potatoes.
5 The fungi kingdom contains single-celled or many-celled organisms that reproduce by spores. Fungi have cells that are surrounded by cell walls, like plants. In fungi, however, the cell walls are made of a different material. Fungi's cell walls are made of chitin, while plants' cell walls are made of cellulose. Fungi are different in another way from plants. Plants make their own food by photosynthesis by using chlorophyll. Fungi have no chlorophyll and so they cannot photosynthesize. Fungi must get their food by feeding on living or dead organisms. Many fungi are decomposers in the food chain. Examples of one-celled (unicellular) fungi are yeasts and some molds. Other fungi are mushrooms and puffballs.
6 The protist kingdom is made up of one-celled (unicellular) organisms and simple many-celled (multicellular) organisms. The nucleus of a protist's cell is enclosed in a nuclear membrane. Some protists, such as the one-celled amoeba and paramecium, feed on other organisms. Others, such as the one-celled euglena or the many-celled algae, make their food by photosynthesis. Other examples of the protist kingdom are diatoms and slime molds.
7 The archaebacteria kingdom includes single-celled organisms. The name means "ancient bacteria." Scientists think that these were like the first life forms on Earth billions of years ago. Their genetic material is not contained inside a nucleus. These cells are called prokaryotes. They lack other structures found in the cells of eukaryotes. Even though bacterial cells are lacking a nucleus and other structures, they still are able to perform all the tasks necessary for life. They use energy, grow and develop, respond to their environment, and reproduce. Some of the archaebacteria have been found in extremely hot water in geysers. They have been placed into a separate kingdom because their chemical makeup is different from the eubacteria. The way their genetic material reproduces is different as well.
8 The sixth kingdom is the eubacteria. These, along with the archaebacteria kingdom, once made up the kingdom monera in the five-kingdom system of classification. Like the archaebacteria, eubacteria are one-celled and lack a nuclear membrane. Some are able to make their own food, and some must find food, also like the archaebacteria. Chemically they are similar to the other kingdoms, unlike the archaebacteria.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy in your journal, date it, and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
_____________________________ |
|  | Date ___________________ |
Six Kingdoms
| 1. | Animals have cells that:
 Have no nucleus Have no nucleus
 Have cell walls Have cell walls
 Have a nucleus bounded by a membrane Have a nucleus bounded by a membrane |
|
| 2. | Plants and animals are:
 Vertebrates Vertebrates
 Unicellular Unicellular
 Multicellular Multicellular |
|
| 3. | What is one trait that all plants share?
 They can make flowers. They can make flowers.
 They can make their own food by photosynthesis. They can make their own food by photosynthesis.
 They are all green. They are all green. |
|
| 4. | Some fungi look like plants, but they are not because:
 Fungi don't have leaves. Fungi don't have leaves.
 Fungi don't need soil to grow. Fungi don't need soil to grow.
 Fungi cannot make their own food. Fungi cannot make their own food. |
|
| 5. | Amoeba and paramecia belong to which kingdom?
 Protist Protist
 Plant Plant
 Animal Animal |
|
| 6. | Members of the archaebacteria and eubacteria kingdoms are all:
 One-celled organisms One-celled organisms
 Bacteria Bacteria
 Able to make their own food Able to make their own food
 Both a and b, but not c Both a and b, but not c |
|
Please copy in your journal, date it, and |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
_____________________________ | | | |
Complete each sentence.
| | Plants give off water during the process called (Prokaryotes, Invertebrate, transpiration) . |
| | A definition of " (, Species, Germination) ; is how long something lives. |
| | More than 230 (species, Eukaryotes, Pollination Ec) of birds inhabit these forests. |
| | He has not shown much (Reproduce, Echinoderms, growth) in his maturity. |
| | Mr. Johnson asked a question about (plants, Transpiration, Reproduce) . |
| | A plant is a good exam ple of an (autotroph, Vascular, Species) . |
| | Snails, clams and squids are (Exothermic, mollusks, Reproduce) . |
| | Some sponges and cnidarians (Eukaryotes, reproduce, Metabolism) asexually as well as sexually. |
| | The Galapagos Islands' insular region is ideal for preserving the many (Kingdom, species, Exoskeleton) contained there. |
| | A (Reproduce, gill, Archeabacteria) helps a fish to breathe. |
| | Some (Vascular, Kingdom, sponges) and cnidarians reproduce asexually as well as sexually. |
| | The snake has a different (Xylem, endoskeleton, Spores) than the lizard. |
| | All living things (Arthropods, Growth, reproduce) . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
____________________________ |
|  | Date ___________________ |
Six KingdomsWhy do you think people try to group living things? In what ways is it useful? In what ways is it confusing? Please explain in your journal





| _____________________________ |
|  | Date ___________________ |
Six KingdomsDo you think the scientific classification system will continue to change? Why or why not? Please explain in your journal



| ___________________________ |
|  | Date ___________________ |
Six KingdomsName the characteristics that ALL animals share. In other words, what makes an animal an animal? Please explain in your journal




Please copy in your journal, date it, and | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |






















