Indicators and Objectives for this Unit
5. 6. C. Electricity and Magnetism
2. Cite evidence supporting that electrical energy can be produced from a variety of energy sources and can itself be
transformed into almost any other form of energy.
a. identify various energy sources and the energy transforming devices used to produce electrical energy
* Wind (generators, wind mills)
* Sun (solar cells)
* Water (turbines)
* Fossil fuels (engines)
b. Cite examples that demonstrate the transformation of electrical energy into other forms of energy.
c. Investigate and describe that some materials allow the quick, convenient, and safe transfer of electricity
(conductors), while others prevent the transfer of electricity (insulators).
d. Identify and describe the energy transformations in simple electric circuits.
3. Identify and describe magnetic fields and their relationship to electric current.
a. Investigate and describe the magnetic fields surrounding various types of magnets using materials, such as iron filings and small compasses.
* A single bar magnet
* Two bar magnets with like poles facing
* Two bar magnets with opposite poles facing
* A horseshoe magnet
b. Explain ways to change the strength of a simple electromagnet by varying the number of coils wrapped, the amount of electricity in the wire, the number of batteries used, and whether or not an iron core is used.
c. Describe how the electromagnet demonstrates the relationship of magnetism and electricity and identify common devices that demonstrate application of this relationship.
* Electric motors (fans, hair dryers, can openers)
* Electrical generators (turbine)
d. Describe that electricity moving through a wire produces a magnetic force on materials placed near the wire.
* Iron filings
1st Big Assignment+ Please look up these
Vocabulary Words to look up and put in your journal
Electricity
Electric current
Atom
Electron
Proton
Neutron
Charge
Voltage
Electric circuit
Insulator
Conductor
Magnet
Electromagnet
Alternative current
Direct current
Electromagnetic induction
Please read this article and complete the work below in your journal
What Is Electricity? By Brandi Waters |  |
 1 Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers work. It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?
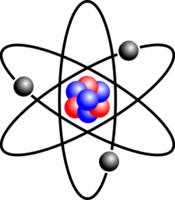
1 Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers work. It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?2 First, you have to know about atoms. All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them without a special microscope. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons both have an electrical charge. Protons have a positive charge. Electrons have a negative charge. Neutrons do not have a positive or a negative charge. Most atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the nucleus of the atom. The nucleus is at the center of an atom. Electrons circle around the nucleus like the planets orbit the sun.
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there
3 Scientists have learned that electrons can move from one atom to another. This creates electricity. You can see electricity in many forms. Lightning is a form of electricity. When you pull a sweater over your hair or rub your feet on the carpet you create static electricity. Electricity can also be made by man. This is how we get electricity to use at our houses. There are many ways that it can be made. It can be made using energy from water flowing down at a dam. It can be made by using the power of the wind. It can also be made by burning fuel. After electricity has been made, it can be moved to other places. A wire is a way of moving electricity. Electrons move from atom to atom along the wire. This creates a current of electricity. Wires run from electrical power plants to homes, schools, and businesses. The wires carry electricity to power our lights and many of our electronic devices.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there

Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
What Is Electricity?
What Is Electricity?





What Is Electricity?






Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers (1) _______________________ . It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?
Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers (1) _______________________ . It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?
First, you have to know about atoms. All (2) _______________________ is made of atoms. Atoms are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them without a special microscope. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons (3) _______________________ have an electrical charge. Protons have a positive charge. Electrons have a (4) _______________________ (5) _______________________ . Neutrons do not have a positive or a negative charge. Most atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the nucleus of the atom. The nucleus is at the center of an atom. Electrons circle around the nucleus like the planets orbit the sun.
Scientists have learned that electrons can move from one atom to (6) _______________________ . This creates electricity. You can see electricity in many forms. Lightning is a form of electricity. When you pull a sweater (7) _______________________ your hair or rub your feet on the carpet you create static electricity. Electricity can also be made by man. This is how we get electricity to use at our houses. There are many ways that it can be made. It can be made using energy from water flowing down at a dam. It can be made by using the power of the wind. It can also be made by burning (8) _______________________ . (9) _______________________ electricity has been made, it can be(10) _______________________ to other places. A wire is a way of (11) _______________________ electricity. Electrons(12) _______________________ from atom to atom (13) _______________________ the wire. This creates a(14) _______________________ of electricity. Wires run from (15) _______________________ power plants to homes,(16) _______________________ , and businesses. The wires carry electricity to power our lights and many of our(17) _______________________ devices.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
What Is Electricity?
 1 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons moving from atom to atom. Electrons have a negative charge. They move toward atoms with a positive charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.
1 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons moving from atom to atom. Electrons have a negative charge. They move toward atoms with a positive charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there

Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
_ |  |
 |
What Is Electricity? By Brandi Waters |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers (1) _______________________ . It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?
Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers (1) _______________________ . It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?First, you have to know about atoms. All (2) _______________________ is made of atoms. Atoms are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them without a special microscope. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons (3) _______________________ have an electrical charge. Protons have a positive charge. Electrons have a (4) _______________________ (5) _______________________ . Neutrons do not have a positive or a negative charge. Most atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the nucleus of the atom. The nucleus is at the center of an atom. Electrons circle around the nucleus like the planets orbit the sun.
Scientists have learned that electrons can move from one atom to (6) _______________________ . This creates electricity. You can see electricity in many forms. Lightning is a form of electricity. When you pull a sweater (7) _______________________ your hair or rub your feet on the carpet you create static electricity. Electricity can also be made by man. This is how we get electricity to use at our houses. There are many ways that it can be made. It can be made using energy from water flowing down at a dam. It can be made by using the power of the wind. It can also be made by burning (8) _______________________ . (9) _______________________ electricity has been made, it can be(10) _______________________ to other places. A wire is a way of (11) _______________________ electricity. Electrons(12) _______________________ from atom to atom (13) _______________________ the wire. This creates a(14) _______________________ of electricity. Wires run from (15) _______________________ power plants to homes,(16) _______________________ , and businesses. The wires carry electricity to power our lights and many of our(17) _______________________ devices.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
|
Electrical Circuits By Brandi Waters |  |
 1 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons moving from atom to atom. Electrons have a negative charge. They move toward atoms with a positive charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.
1 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons moving from atom to atom. Electrons have a negative charge. They move toward atoms with a positive charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
2 Electrons cannot jump across a distance. There must be a path for electrons to follow. The path must be a series of atoms that can accept an electron. We call this path a circuit. People have learned how to build and manipulate circuits to move electricity. We use circuits to bring electricity into our homes. We use circuits to move electricity through our computers, telephones, toys, and even our cars.
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there

Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
Electrical Circuits
Electrical Circuits





Electrical Circuits





Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons(1) _______________________ from atom to atom. Electrons have a (2) _______________________ charge. They move toward atoms with a (3) _______________________ charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.
You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons(1) _______________________ from atom to atom. Electrons have a (2) _______________________ charge. They move toward atoms with a (3) _______________________ charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.
Electrons cannot jump (4) _______________________ a distance. There must be a path for electrons to follow. The path must be a (5) _______________________ of atoms that can (6) _______________________ an electron. We call this path a circuit. (7) _______________________ have learned how to (8) _______________________ and manipulate circuits to move electricity. We use circuits to (9) _______________________ electricity into our homes. We use circuits to(10) _______________________ electricity through our computers, telephones, toys, and even our cars.
Every time you flip a light switch in your house, you are using a circuit. The light bulb glows when electrons are flowing through it. The light bulb (11) _______________________ glows when the switch is on. This is because the circuit is complete when the switch is on. Wiring in your house forms a path for (12) _______________________ to flow. The wires are attached to the light bulb. The wires are also connected to the switch on the (13) _______________________ . When the switch is turned off, there is a (14) _______________________ in the circuit. When the circuit is (15) _______________________ , electricity cannot flow through the light bulb. When the switch is turned on, the switch forms a bridge that completes the circuit. Electrons can flow through the wires, through the (16) _______________________ , and through the light (17) _______________________ . The light bulb glows and lights your room. Circuits help people control when and where electricity flows.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Electrical Circuits
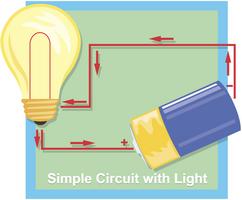 1 The electrical wires in your house make a path for the electricity to run through. Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady flow of electric charges moving from one place to another. Electric currents move in a path called a circuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do something. For example, when you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light bulb. The light comes on. Turn the light switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a small gap to turn off the light. Electric current can no longer flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the circuit. Electric current flows like water in a river bed.
1 The electrical wires in your house make a path for the electricity to run through. Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady flow of electric charges moving from one place to another. Electric currents move in a path called a circuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do something. For example, when you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light bulb. The light comes on. Turn the light switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a small gap to turn off the light. Electric current can no longer flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the circuit. Electric current flows like water in a river bed.
Electric Current
Electric Current





Electric Current






 The electrical wires in your house (1) _______________________ a path for the electricity to run(2) _______________________ . Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady(3) _______________________ of electric charges moving from one place to(4) _______________________ . Electric currents move in a (5) _______________________ called acircuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do(6) _______________________ . For example, (7) _______________________ you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light(8) _______________________ . The light comes on. Turn the (9) _______________________ switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a (10) _______________________ gap to (11) _______________________ off the light. Electric current can no (12) _______________________ flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the (13) _______________________ . Electric current (14) _______________________ like(15) _______________________ in a (16) _______________________ bed.
The electrical wires in your house (1) _______________________ a path for the electricity to run(2) _______________________ . Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady(3) _______________________ of electric charges moving from one place to(4) _______________________ . Electric currents move in a (5) _______________________ called acircuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do(6) _______________________ . For example, (7) _______________________ you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light(8) _______________________ . The light comes on. Turn the (9) _______________________ switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a (10) _______________________ gap to (11) _______________________ off the light. Electric current can no (12) _______________________ flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the (13) _______________________ . Electric current (14) _______________________ like(15) _______________________ in a (16) _______________________ bed.
Electric Current
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there
3 Every time you flip a light switch in your house, you are using a circuit. The light bulb glows when electrons are flowing through it. The light bulb only glows when the switch is on. This is because the circuit is complete when the switch is on. Wiring in your house forms a path for electricity to flow. The wires are attached to the light bulb. The wires are also connected to the switch on the wall. When the switch is turned off, there is a break in the circuit. When the circuit is broken, electricity cannot flow through the light bulb. When the switch is turned on, the switch forms a bridge that completes the circuit. Electrons can flow through the wires, through the switch, and through the light bulb. The light bulb glows and lights your room. Circuits help people control when and where electricity flows.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Copyright © 2011 edHelper

 |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
Please click this site below , hit enter, complete the electrical circuit reading and activity.
NOW take 15 or more notes about what you learned from the reading and activity.
 |
Electricity
magnetic field parallel circuit electric field
electromagnet fuse conductor
direct current voltage alternating current
insulator electricity kilowatt-hour
circuit lodestone ground
generator short circuit series circuit
resistor compass ampere
charge magnet static electricity
lightning rod
Matching
Assignment-In your journal. Match each definition with a word above
1. An electric current flowing only in one direction.
2. The amount of energy used when you consume one kilo-watt of power in one
hour.
3. A piece of metal that stands at the highest point of a building and is connected to
the Earth. The purpose of the piece of metal is to ground the large amount of
electrical energy in the event of a lightning strike.
4. A machine that produces electricity by changing energy of motion into electrical
energy.
5. An electrical connection that allows electrons to be carried away in the event of a
problem.
6. A unit used to measure current.
7. A magnet created when electric current flows through a coil of wire.
8. Energy formed by the motion of protons and electrons.
9. A measure of the amount of electricity in an atom that is determined by the extra
positive or negative particles that an atom has.
10. The area around charged particles where electric forces occur.
 |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
Electrical Circuits By Brandi Waters |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons(1) _______________________ from atom to atom. Electrons have a (2) _______________________ charge. They move toward atoms with a (3) _______________________ charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.
You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons(1) _______________________ from atom to atom. Electrons have a (2) _______________________ charge. They move toward atoms with a (3) _______________________ charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.Electrons cannot jump (4) _______________________ a distance. There must be a path for electrons to follow. The path must be a (5) _______________________ of atoms that can (6) _______________________ an electron. We call this path a circuit. (7) _______________________ have learned how to (8) _______________________ and manipulate circuits to move electricity. We use circuits to (9) _______________________ electricity into our homes. We use circuits to(10) _______________________ electricity through our computers, telephones, toys, and even our cars.
Every time you flip a light switch in your house, you are using a circuit. The light bulb glows when electrons are flowing through it. The light bulb (11) _______________________ glows when the switch is on. This is because the circuit is complete when the switch is on. Wiring in your house forms a path for (12) _______________________ to flow. The wires are attached to the light bulb. The wires are also connected to the switch on the (13) _______________________ . When the switch is turned off, there is a (14) _______________________ in the circuit. When the circuit is (15) _______________________ , electricity cannot flow through the light bulb. When the switch is turned on, the switch forms a bridge that completes the circuit. Electrons can flow through the wires, through the (16) _______________________ , and through the light (17) _______________________ . The light bulb glows and lights your room. Circuits help people control when and where electricity flows.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Multiple Choice
Please copy in your journal and Select the definition that most nearly defines the given word.
11. charge
A. A measure of the amount of electricity in an atom that is determined by the extra
positive or negative particles that an atom has.
B. A hard, black, naturally magnetic rock.
12. series circuit
A. A magnet created when electric current flows through a coil of wire.
B. An electric circuit that has only one path for the current.
13. circuit
A. The area around charged particles where electric forces occur.
B. A closed path along which electricity flows.
14. magnet
A. An object with two poles that attracts iron and steel.
B. The force that pushes electricity or a current. In most homes this force is 110 volts.
15. lodestone
A. A path that allows most of the current in an electric circuit to flow around or away
from the principal elements or devices in the circuit.
B. A hard, black, naturally magnetic rock.
16. direct current
A. The amount of energy used when you consume one kilo-watt of power in one hour.
B. An electric current flowing only in one direction.
17. alternating current
A. An electric current that reverses its direction of flow at regular intervals.
B. A unit used to measure current.
18. voltage
A. An electrical connection that allows electrons to be carried away in the event of a
problem.
B. The force that pushes electricity or a current. In most homes this force is 110 volts.
19. magnetic field
A. The space around a magnet where the force of the magnet can be felt.
B. This has a magnetized needle that is attracted to the earth's north magnetic pole.
20. static electricity
A. An electric circuit that has only one path for the current.
B. A charge that stays on an object instead of flowing in a current.
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
|
Electric Current By Cindy Grigg |  |
 1 The electrical wires in your house make a path for the electricity to run through. Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady flow of electric charges moving from one place to another. Electric currents move in a path called a circuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do something. For example, when you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light bulb. The light comes on. Turn the light switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a small gap to turn off the light. Electric current can no longer flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the circuit. Electric current flows like water in a river bed.
1 The electrical wires in your house make a path for the electricity to run through. Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady flow of electric charges moving from one place to another. Electric currents move in a path called a circuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do something. For example, when you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light bulb. The light comes on. Turn the light switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a small gap to turn off the light. Electric current can no longer flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the circuit. Electric current flows like water in a river bed.Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
_____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
|
Electric Current
Please click this site below , hit enter, click the 2nd of 5 pictures, complete the electrical conductors and insulators reading and activity.
NOW take 15 or more notes about what you learned from the reading and activity.
 |
Please copy this "cloze" assignment in your journal and complete it there
Electric Current By Cindy Grigg |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 The electrical wires in your house (1) _______________________ a path for the electricity to run(2) _______________________ . Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady(3) _______________________ of electric charges moving from one place to(4) _______________________ . Electric currents move in a (5) _______________________ called acircuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do(6) _______________________ . For example, (7) _______________________ you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light(8) _______________________ . The light comes on. Turn the (9) _______________________ switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a (10) _______________________ gap to (11) _______________________ off the light. Electric current can no (12) _______________________ flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the (13) _______________________ . Electric current (14) _______________________ like(15) _______________________ in a (16) _______________________ bed.
The electrical wires in your house (1) _______________________ a path for the electricity to run(2) _______________________ . Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady(3) _______________________ of electric charges moving from one place to(4) _______________________ . Electric currents move in a (5) _______________________ called acircuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do(6) _______________________ . For example, (7) _______________________ you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light(8) _______________________ . The light comes on. Turn the (9) _______________________ switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a (10) _______________________ gap to (11) _______________________ off the light. Electric current can no (12) _______________________ flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the (13) _______________________ . Electric current (14) _______________________ like(15) _______________________ in a (16) _______________________ bed.Copyright © 2011 edHelper
 |
|
| ||||
|
|
Please click this site below , hit enter, click the 3rd of 5 pictures, complete the electrical switches reading and activity.
NOW take 15 or more notes about what you learned from the reading and activity.
Review
21. The magnetic force is strongest at a magnet's poles.
A. True
B. False
22. An electromagnet is a temporary magnet.
A. True
B. False
23. What is the most dangerous part of electricity?
A. The charge
B. Electricity is not dangerous at all.
C. The current
D. The voltage
24. Thomas designs an electric circuit that has 2 batteries connected in series and 1 bulb.
If one of the batteries dies, the brightness of the bulb remains the same.
A. False
B. True
25. What does a switch use to make or break an electric current?
A. Resistors only
B. Conductors and insulators
C. Conductors and resistors
D. Insulators and resistors
26. What did Benjamin Franklin invent in 1752?
A. A kite
B. A key
C. Lightning
D. A lightning rod
27. Lodestone is a natural mineral that possesses magnetic properties.
A. False
B. True
28. What is the area around charged particles where electric forces occur?
A. A power field
B. An electromagnetic field
C. A magnetic field
D. An electric field
29. Emily can control the brightness of her living room lights by turning a knob. If Emily
dims the lights, the knob increases the resistance to the electric current.
A. True
B. False
30. What good insulator material is often used to coat electrical wires?
A. Plastic
B. Paper
C. Copper
D. Aluminum
Please click this site below , hit enter, click the 4th of 5 pictures, complete the changing circuits reading and activity.
NOW take 15 or more notes about what you learned from the reading and activity.
Electricity - Circuit Construction
Electricity - ADV. circuit construction
Electricity- Signal Circuit
Electricity - Adv-Resistance in a Wire
Electricity - Ohms Law -Adv
Electric Generator
Faradays Law
Faradays Electromagnetic Lab
Electric Circuit
Electricity -
Battery-Resistor Circuit
Battery Voltage
POST TEST
· What is electricity?
· What is the difference between static electricity and current electricity?
· What is an atom?
· How does electricity move through a circuit?
· What is the difference between an insulator and a conductor?
· What is the difference between an open circuit and a closed circuit?
· What is static electricity?
· What is magnetism?
· How is earth like a magnet?
· How are electricity and magnetism related?
· What is an electromagnet?
· What are electric motors?
· How does an electric motor work?
· What’s the difference between alternative current and direct current?
Does the number of coils affect magnetic force?





No comments:
Post a Comment