Objectives and Indicators for this Unit§ Living things are made of single or multiple cells
§ Microscopes make it possible to see that living things are made of mostly cells
§ Most single celled organisms have needs similar to those of multi-cellular organisms.
The cells in multi-cellular organisms may vary in appearance and function, but they benefit from cooperating
VSC
3.7.B. Cells 1. Gather and organize data to defend or argue the proposition that all living things are cellular (composed of cells) and that cells carry out the basic life functions. a. Use microscopes or other magnifying instruments to observe, describe, and compare the cellular composition of different body tissues and organs in a variety of organisms (animals and plants). b. Based on data from readings and designed investigations, cite evidence to illustrate that the life functions of multicellular organisms (plant and animal) are carried out within complex systems of different tissues, organs and cells. § Getting rid of wastes § Making raw materials c. Based on research and examples from video technology explain that the repeated division of cells enables organisms to grow and make repairs. d. Collect data from investigations using single celled organisms, such as yeast or algae to explain that a single cell carries out all the basic life functions of a multicellular organism. § Reproducing § Getting rid of wastes e. Based on data compiled from a number of lessons completed, take and defend a position on the statement "The way in which cells function is the same in all organisms.” 2. Recognize and provide examples that human beings, like other organisms have complex body systems of cells, tissues and organs that interact to support an organism's growth and survival. a. Describe and explain that the complex set of systems found in multicellular organisms are made up of different kinds of tissues and organs which are themselves composed of differentiated cells. b. Select several body systems and explain the role of cells, tissues and organs that effectively carry out a vital function for the organism, such as § Defense (nervous, endocrine, circulatory, muscular, skeletal, immune) § Reproduction (reproductive, endocrine, circulatory) § Waste removal (excretory, respiratory, circulatory) § Breathing (respiratory, circulatory) c. Develop a response that explains the meaning of the statement, "The specialization of cells serves the operation of the organs, and the organs serve the needs of the cells." d. Investigate ways in which the various organs and tissues function to serve the needs of cells for food, air, and waste removal. |
· All living things are composed of cells.
· Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in life.
· Cellular composition, structure and function differ between animal and plant cells.
· Cells form tissues, tissues form organs, organs form systems, and systems form organisms.
· Cell organelles produce energy, build and transport materials, and store and recycle wastes.
Substances move into and out of a cell by diffusion, osmosis, or active transport
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
First Big Assignment= Please look up these vocabulary words and put the words and their
definitions into your journal
- CELLS
- PROKARYOTIC CELLS
- EUKARYOTIC CELLS
- MICROSCOPE
- CELL MEMBRANE
- CYTOPLASM
- CELL WALL
- ORGANELLE
- NUCLEUS
- CHROMATIN
- CHROMATID
- CHROMOSOME
- NUCLEOLUS
- VACUOLES
- LYSOSOMES
- BACTERIAL CELL
- PERMEABILITY
- EQUILIBRIUM
- OSMOSIS
- STARCH
- LIPIDS
- NUCLEIC ACID
- AMINO ACID
- ENZYME
- PROTEIN
- ENDOCYTOSIS
- EXOCYTOSIS
- METABOLISM
- PHOTOSYNTHESIS
- PIGMENT
- STOMATA
- AUTOTROPH
- HETEROTROPH
- RESPIRATION
- FERMENTATION
- CELL CYCLE
- INTERPHASE
- PROPHASE
- METAPHASE
- ANAPHASE
- TELOPHASE
- CYTOKINESIS
- EGG
- SPERM
- ZYGOTE
- DIPLOID
Please read this article and complete the assignments below in your journals
| Cells By Brandi Waters |  |
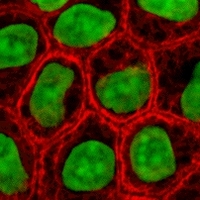 1 Cells are a part of every living thing. Just like atoms are the building blocks of matter, cells are the building blocks of living things. Some living things are made of only one cell. Most of the germs that can make us sick are made of only a single cell. Other living things are made of many, many cells. Trillions of cells come together to build a human being!
1 Cells are a part of every living thing. Just like atoms are the building blocks of matter, cells are the building blocks of living things. Some living things are made of only one cell. Most of the germs that can make us sick are made of only a single cell. Other living things are made of many, many cells. Trillions of cells come together to build a human being! |
| Main Idea and 4 Details Graphic Organizer |
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.
2 Most cells are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them without a microscope. There are a few cells, though, that are big enough to easily see. An egg, like you might eat for breakfast, is one very large cell.
3 There are many different kinds of cells. Plant cells are different from the cells of animals. Some cells are independent. Some cells work together to perform a job. Some cells can move. Some cells can glow in the dark! Each type of cell is different, but there are some things that all cells have in common. All cells are covered by a membrane that helps to protect the cell and hold it together. All cells are able to reproduce. All cells can take in nutrients and turn them into energy. All cells respond to changes inside and around them. Cells are alive!
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.
 |
| Main Idea and 7 Details Graphic Organizer |
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| Cells By Brandi Waters |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Cells are a (1) _______________________ of every living thing. Just like atoms are the building blocks of (2) _______________________ , cells are the(3) _______________________ blocks of living things. Some living things are made of (4) _______________________ one cell. Most of the germs that can make us sick are made of only a single cell. Other living things are made of many, many cells. Trillions of cells come together to (5) _______________________ a (6) _______________________ being!
Cells are a (1) _______________________ of every living thing. Just like atoms are the building blocks of (2) _______________________ , cells are the(3) _______________________ blocks of living things. Some living things are made of (4) _______________________ one cell. Most of the germs that can make us sick are made of only a single cell. Other living things are made of many, many cells. Trillions of cells come together to (5) _______________________ a (6) _______________________ being!Most cells are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them (7) _______________________ a microscope. There are a few cells, though, that are big enough to (8) _______________________ see. An egg, like you (9) _______________________ eat for breakfast, is one very large cell.
There are many different kinds of cells. Plant cells are different from the cells of animals. Some cells are (10) _______________________ . Some cells work together to (11) _______________________ a job. Some cells can move. Some cells can glow in the dark! Each (12) _______________________ of cell is different, but there are some things that all cells have in common. All cells are covered by a membrane that helps to protect the cell and hold it together. All cells are able to (13) _______________________ . All cells can take in nutrients and (14) _______________________ them into (15) _______________________ . All cells respond to changes inside and around them. Cells are (16) _______________________ !
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
CELLS ARE US
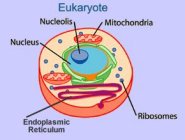
Just as atoms have smaller parts called protons, neutrons, and electrons, cells have smaller parts, too. When you look at cells with a powerful microscope, you can clearly see hundreds of them. With the most powerful lens, you can see a single cell close up. You can see most of the different parts of a cell, called organelles meaning "little organs," with a very powerful microscope. Let's read about some of the different parts.
7 First, all cells have a cell membrane. It holds all the parts of the cell together. It lets water and other molecules come and go into and out of the cell. Think of it like your body's skin.
8 Next, all eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells include everything except bacteria and viruses. People have eukaryotic cells. The nucleus of a cell contains the cell's genetic information, DNA, so that the cell can produce more cells like it. This is important because cells don't live very long. Our skin cells die and must be replaced about every thirty days. The nucleus also controls the cell's processes. Think of it like your body's brain. The nucleus is sometimes called the "command center" of the cell.
9 Another important part is the mitochondria, called the "powerhouses of the cell." The mitochondria's job is to break down food molecules so that the cell has energy to live. Think of it like your body's stomach. The more energy the cell needs, the more mitochondria it has.
10 Cells are filled with a liquid called cytoplasm. Cytoplasm fills up the space inside the cell and gives the cell a medium for movement of molecules. Molecules can move more easily in the liquid medium than they could move if the cell had empty space inside it.
11 Vacuoles are storage compartments inside the cell. Cells can store molecules they need or waste products inside the vacuoles until they are needed or eliminated.
7 First, all cells have a cell membrane. It holds all the parts of the cell together. It lets water and other molecules come and go into and out of the cell. Think of it like your body's skin.
8 Next, all eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells include everything except bacteria and viruses. People have eukaryotic cells. The nucleus of a cell contains the cell's genetic information, DNA, so that the cell can produce more cells like it. This is important because cells don't live very long. Our skin cells die and must be replaced about every thirty days. The nucleus also controls the cell's processes. Think of it like your body's brain. The nucleus is sometimes called the "command center" of the cell.
9 Another important part is the mitochondria, called the "powerhouses of the cell." The mitochondria's job is to break down food molecules so that the cell has energy to live. Think of it like your body's stomach. The more energy the cell needs, the more mitochondria it has.
10 Cells are filled with a liquid called cytoplasm. Cytoplasm fills up the space inside the cell and gives the cell a medium for movement of molecules. Molecules can move more easily in the liquid medium than they could move if the cell had empty space inside it.
11 Vacuoles are storage compartments inside the cell. Cells can store molecules they need or waste products inside the vacuoles until they are needed or eliminated.
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.
 |
| Main Idea and 5 Details Graphic Organizer |
| Cells By Brandi Waters |  |
 1 Cells are a part of every living thing. Just like atoms are the building blocks of matter, cells are the building blocks of living things. Some living things are made of only one cell. Most of the germs that can make us sick are made of only a single cell. Other living things are made of many, many cells. Trillions of cells come together to build a human being!
1 Cells are a part of every living thing. Just like atoms are the building blocks of matter, cells are the building blocks of living things. Some living things are made of only one cell. Most of the germs that can make us sick are made of only a single cell. Other living things are made of many, many cells. Trillions of cells come together to build a human being!Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.
 |
| Main Idea and 5 Details Graphic Organizer |
2 Most cells are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them without a microscope. There are a few cells, though, that are big enough to easily see. An egg, like you might eat for breakfast, is one very large cell.
3 There are many different kinds of cells. Plant cells are different from the cells of animals. Some cells are independent. Some cells work together to perform a job. Some cells can move. Some cells can glow in the dark! Each type of cell is different, but there are some things that all cells have in common. All cells are covered by a membrane that helps to protect the cell and hold it together. All cells are able to reproduce. All cells can take in nutrients and turn them into energy. All cells respond to changes inside and around them. Cells are alive!
 |
| Main Idea and 5 Details Graphic Organizer |
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete it there .
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete it there
| Cells By Brandi Waters |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Cells are a (1) _______________________ of every living thing. Just like atoms are the building blocks of matter, cells are the building blocks of living things. Some living things are made of only one cell. Most of the germs that can make us sick are made of only a (2) _______________________ cell.(3) _______________________ living things are made of many, many cells. Trillions of cells come together to build a (4) _______________________ being!
Cells are a (1) _______________________ of every living thing. Just like atoms are the building blocks of matter, cells are the building blocks of living things. Some living things are made of only one cell. Most of the germs that can make us sick are made of only a (2) _______________________ cell.(3) _______________________ living things are made of many, many cells. Trillions of cells come together to build a (4) _______________________ being!Most cells are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them (5) _______________________ a (6) _______________________ . There are a few cells, though, that are big (7) _______________________ to (8) _______________________ see. An egg, like you might eat for breakfast, is one very large cell.
There are many (9) _______________________ (10) _______________________ of cells. Plant cells are different from the cells of animals. Some cells are independent. Some cells work together to (11) _______________________ a job. Some cells can (12) _______________________ . Some cells can glow in the dark! Each type of cell is different, but there are some things that all cells have in (13) _______________________ . All cells are covered by a membrane that helps to (14) _______________________ the cell and hold it together. All cells are able to (15) _______________________ . All cells can take in nutrients and turn them into energy. All cells respond to changes inside and around them. Cells are alive!
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
Assignment-Please click the website below-Then hit "run"
and play the game. Watch how things can pass through the membrane. One choice works considerably better than the other choice.
Then 1) Explain in your journal exactly what happened. and
2) Explain in your journal why you think it happened in the way it did?
Cell MEMBRANE CHANNELS
Inside a cell
Assignment= Please click this website and Play this games about cell parts
Then 1) Explain in your journal exactly what happened. and
2) Explain in your journal why you think it happened in the way it did?
Cells Are Us! By Cindy Grigg |  |
 1 Did you ever stop to think what your body might be made of? Your body is made of cells. Cells are called the "building blocks" of life. Adults have about ten trillion (10,000,000,000,000) cells in their bodies! Your body was made when one tiny cell from your father joined another tiny cell from your mother. These two cells became one very special cell, and that very special cell became you!
1 Did you ever stop to think what your body might be made of? Your body is made of cells. Cells are called the "building blocks" of life. Adults have about ten trillion (10,000,000,000,000) cells in their bodies! Your body was made when one tiny cell from your father joined another tiny cell from your mother. These two cells became one very special cell, and that very special cell became you!2 That very special cell had all the information and "secret codes" to make you the way you are. Those "secret codes" were inside the DNA. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic (de-ox-e-rye-bo-new-clay-ick) acid. DNA is a very long list of instructions found in the nucleus of the cell that gives each cell in your body its shape and function.
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.
3 But how did you grow from one tiny cell? Cells grow, or multiply, by dividing! First there was only one cell, and then it divided by a process called cell division or mitosis. So then there were two cells. Then each of those cells divided, and then there were four cells. Then each of those cells divided, and then there were eight cells. Then those cells divided, and ... Well, you get the picture.
4 Think about building something with plastic blocks. The blocks have different shapes and are different sizes. They look different from each other. Each type of block has a different job, but when you put them all together, you can build a castle! Like the castle, our bodies are made of many different kinds of "blocks." The big difference is that the blocks our body is made of are very, very tiny. They are called cells. How tiny are they? VERY tiny! You could fit about a hundred of them on the period at the end of this sentence.
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.
5 Cells are the smallest things that can carry out life processes. What are life processes? Living things need to take in food and water, take out wastes, and be able to reproduce themselves. In this way, cells are different from atoms and molecules. Atoms are not living things; they do not need food, water, and air; and they do not reproduce themselves. Cells are alive. Cells are bigger than atoms. We can see cells with a microscope.
6
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.
12 There are many different kinds of cells in our bodies. Just as you would need different sizes and shapes of blocks to build a castle, your body's cells are different sizes and shapes, too. Each kind of cell is shaped differently because it has a different job to do. Some of the different kinds of cells we have in our bodies are muscle cells, red blood cells, and nerve cells. We have more than two hundred different kinds of cells! Each of these cells looks very, very different from each other.
13 Your body was made from just two cells, one from your mother and one from your father. Those two cells joined together into one special cell, and it held all the genetic information to make you, you. The information in the DNA decided whether you would have dimples or not. It decided your hair color, eye color, and even the shape of your earlobes! You are unique, different from every other human on the earth, because of the information in those two tiny cells. You are made of cells!
13 Your body was made from just two cells, one from your mother and one from your father. Those two cells joined together into one special cell, and it held all the genetic information to make you, you. The information in the DNA decided whether you would have dimples or not. It decided your hair color, eye color, and even the shape of your earlobes! You are unique, different from every other human on the earth, because of the information in those two tiny cells. You are made of cells!
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Assignment= Please copy into your journal and complete this graphic organizer from the reading above.
_ |  |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
 |
 |
 |
Assignment=Please copy this "cloze" assignment into your journal and answer the questions there.
Cells Are Us! By Cindy Grigg |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Did you (1) _______________________ stop to think what your body might be made of? Your body is made of cells. Cells are called the "building blocks" of life. Adults have about ten trillion (10,000,000,000,000) cells in their bodies! Your body was made when one tiny cell from your father joined another tiny cell from your mother. These two cells became one very special cell, and that very special cell became you!
Did you (1) _______________________ stop to think what your body might be made of? Your body is made of cells. Cells are called the "building blocks" of life. Adults have about ten trillion (10,000,000,000,000) cells in their bodies! Your body was made when one tiny cell from your father joined another tiny cell from your mother. These two cells became one very special cell, and that very special cell became you!That very special cell had all the information and "secret codes" to make you the way you are. Those "secret codes" were inside the DNA. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic (de-ox-e-rye-bo-new-clay-ick) acid. DNA is a very long list of instructions found in the nucleus of the cell that gives each cell in your body its shape and function.
But how did you grow from one tiny cell? Cells grow, or multiply, by dividing! First there was only one cell, and then it divided by a process called cell (2) _______________________ or(3) _______________________ . So then there were two cells. Then each of those cells divided, and then there were four cells. Then each of those cells divided, and then there were eight cells. Then those cells divided, and ... Well, you get the picture.
Think about building something with plastic blocks. The blocks have different shapes and are different sizes. They look different from each other. Each type of block has a different job, but when you put them all together, you can build a castle! Like the castle, our bodies are made of many different kinds of "blocks." The big (4) _______________________ is that the blocks our body is made of are very, very tiny. They are called cells. How tiny are they? VERY tiny! You could fit about a hundred of them on the (5) _______________________ at the end of this sentence.
Cells are the smallest things that can carry out life processes. What are life processes? Living things need to take in food and water, take out wastes, and be able to reproduce themselves. In this way, cells are different from atoms and molecules. Atoms are not living things; they do not need food, water, and air; and they do not reproduce themselves. Cells are alive. Cells are bigger than atoms. We can see cells with a microscope.
Just as atoms have smaller parts called protons, neutrons, and electrons, cells have smaller parts, too. When you look at cells with a powerful microscope, you can (6) _______________________ see hundreds of them. With the most powerful lens, you can see a single cell close up. You can see most of the different parts of a cell, called (7) _______________________ meaning "little organs," with a very powerful microscope. Let's read about some of the different parts.
First, all cells have a cell membrane. It holds all the parts of the cell together. It lets water and other molecules come and go into and out of the cell. Think of it like your body's skin.
Next, all eukaryotic cells have a nucleus. Eukaryotic cells include everything except bacteria and viruses. People have (8) _______________________ cells. The nucleus of a cell contains the cell's genetic information, DNA, so that the cell can produce more cells like it. This is important because cells don't live very long. Our skin cells die and must be replaced about every thirty days. The nucleus also controls the cell's processes. Think of it like your body's brain. The nucleus is sometimes called the "(9) _______________________ (10) _______________________ " of the cell.
Another important part is the mitochondria, called the "powerhouses of the cell." The mitochondria's job is to break down food molecules so that the cell has energy to live. Think of it like your body's stomach. The more energy the cell needs, the more mitochondria it has.
Cells are filled with a liquid called (11) _______________________ . Cytoplasm fills up the space inside the cell and gives the cell a medium for movement of molecules. Molecules can move more easily in the(12) _______________________ medium than they could move if the cell had empty space inside it.
Vacuoles are storage compartments inside the cell. Cells can store molecules they need or waste products inside the vacuoles until they are needed or eliminated.
There are many different kinds of cells in our bodies. Just as you would need different sizes and shapes of blocks to build a castle, your body's cells are different sizes and shapes, too. Each kind of cell is shaped differently because it has a different job to do. Some of the different kinds of cells we have in our bodies are muscle cells, red blood cells, and (13) _______________________ cells. We have more than two hundred different kinds of cells! Each of these cells looks very, very different from each other.
Your body was made from just two cells, one from your mother and one from your father. Those two cells joined together into one special cell, and it held all the (14) _______________________ information to make you, you. The information in the DNA decided whether you would have dimples or not. It decided your hair color, eye color, and even the shape of your earlobes! You are unique, different from every other human on the(15) _______________________ , because of the information in those two tiny cells. You are made of cells!
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
 |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
 |
1. | produce |
2. | sentence |
3. | membrane |
4. | meaning |
5. | process |
6. | deoxyribonucleic |
7. | function |
8. | center |
9. | organelles |
Assignment=Copy these lists in your journal and connect the term to it's correct meaning
Vacuole | Found in plants and some single-celled organisms- filled with liquid. | ||
Ribosome | Small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm involved in protein synthesis. | ||
Lysosomes | Filled with enzymes. | ||
Golgi Apparatus | Stack of membrane=bound vesicles. | ||
Smooth Enoplasmic Reticulum | Cellular internal membrane system- no ribosomes are found on the surface. | ||
Mitochondria | Rod shaped- with folded membrane called cristae. | ||
Cell Wall | Rigid barrier outside the cell membrane- made of carbohydrates- found in plants, algae, fungi, and prokaryotes. | ||
Cell Membrane | Bi-lipid layer with embedded proteins- surrounds the cell. | ||
Cytoskeleton | Network of Protein filaments called microtubules and microfilaments. | ||
Cytoplasm | Area between the cell membrane and the nucleus- jelly like material 80% water. | ||
Nucleus | Bound by a double membrane- contains the cell's DNA. | ||
Nucleolus | Found inside the Nucleus. | ||
Chloroplast | Found in all higher plant cells- contain chlorophyll- double outer membrane- have stroma, thylakoids, and grana- where photosynthesis takes place. | ||
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum | Cellular internal membrane system- site of ribosomes and therefore protein synthesis. | ||
Centrioles | Made from Microtubules- form a pair of structures- located near the nucleus. |
Very Cool Experiment to Try
The Human Cheek Cell
__________________________________
1. List the 3 parts of the Cell Theory
_____________________________________
_____________________________________
_____________________________________
2. Describe or define each of the following
--cell membrane _____________________________
--cytoplasm _________________________________
--nucleus ___________________________________
--organelle ________________________________
--organelle ________________________________
Procedure: 1. Put a drop of methylene blue on a slide. Caution: methylene blue will stain clothes and skin. 2. Gently scrape the inside of your cheek with the flat side of a toothpick. Scrape lightly. 3. Stir the end of the toothpick in the stain and throw the toothpick away. 4. Place a coverslip onto the slide 5. Use the SCANNING objective to focus. You probably will not see the cells at this power. 6. Switch to low power. Cells should be visible, but they will be small and look like nearly clear purplish blobs. If you are looking at something very dark purple, it is probably not a cell 7. Once you think you have located a cell, switch to high power and refocus. (Remember, do NOT use the coarse adjustment knob at this point) |
3. Sketch the cell at low and high power. Label the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell membrane. Draw your cells to scale.Low Power
 High Power
High Power
 5. Why is methylene blue necessary?
5. Why is methylene blue necessary?
 High Power
High Power 5. Why is methylene blue necessary?
5. Why is methylene blue necessary?6. The light microscope used in the lab is not powerful enough to view other organelles in the cheek cell. What parts of the cell were visible.
6. List 2 organelles that were NOT visible but should have been in the cheek cell.
7. Is the cheek cell a eukaryote or prokaryote? How do you know?
8. Keeping in mind that the mouth is the first site of chemical digestion in a human. Your saliva starts the process of breaking down the food you eat. Keeping this in mind, what organelle do you think would be numerous inside the cells of your mouth?
Assignment=Please copy these test questions into your journal and answer the questions there.
Topic B. Cells |
Indicator 2. Investigate and provide evidence that living things are made mostly of cells that can be seen and studied only through a microscope. |
Objective b. Use microscopes and pictures to investigate, |
Selected Response Item | |
|---|---|
Most organisms are made of many different types of cells. Each type of cell has a special role within the organism.  Which of these organisms would most likely contain cells shaped like a rectangle?
/toolkit/vsc/assessment_items/msa_science_5_033.xml | Correct Answer: |
Brief Constructed Response (BCR) Item | |
|---|---|
Most organisms are made of many different types of cells. Each type of cell has a special role within the organism. Multicellular organisms are made of groups of cells working together to do one job. These are called specialized cells. The diagrams show four types of specialized cells. Not all multicellular organisms need the same specialized cells.  Explain why multicellular organisms only need certain specialized cells. In your explanation, be sure to include
Write your answer on your answer document | |
Brief Constructed Response (BCR) Item | |
|---|---|
Fireflies release light from specialized cells in a part of their body called the lantern. The light produced releases very little heat. The firefly signals attract other fireflies and also warn predators that they taste bad. Some female fireflies produce “false signals” to attract male fireflies. These “false signals” are a response to a male light signal. The attracted male firefly comes to the light of the female firefly. The female firefly then eats the male firefly.  Explain why fireflies have different types of specialized cells. In your explanation, be sure to include
Write your answer in the space provided. | |
POST- TEST CELLS
Cells - Please copy and answer in your journal
Cells
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
| 36 KB | Off | ||||||
| 2a,C~E~L~L~O.doc | Aug 2, 2010 8:25:36 PM | 46 KB | Off | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3a,broken bones.doc | Aug 2, 2010 8:25:46 PM | 55 KB | Off | ||||
| 4a,mitosis flip book.doc | Aug 2, 2010 8:25:57 PM | 35 KB | Off | ||||
| 5a,eadible cells.doc | Aug 2, 2010 8:26:08 PM | 39 KB | Off | ||||
| 6a,lets analyze our lunch.doc | Aug 2, 2010 8:26:17 PM | 57 KB | Off |














No comments:
Post a Comment