8th Grade Unit#2 -Electricity
Electrical Circuits - 8th Grade Unit#2
5. 6. C. Electricity and Magnetism
2. Cite evidence supporting that electrical energy can be produced from a variety of energy sources and can itself be
transformed into almost any other form of energy.
a. identify various energy sources and the energy transforming devices used to produce electrical energy
* Wind (generators, wind mills)
* Sun (solar cells)
* Water (turbines)
* Fossil fuels (engines)
b. Cite examples that demonstrate the transformation of electrical energy into other forms of energy.
c. Investigate and describe that some materials allow the quick, convenient, and safe transfer of electricity
(conductors), while others prevent the transfer of electricity (insulators).
d. Identify and describe the energy transformations in simple electric circuits.
3. Identify and describe magnetic fields and their relationship to electric current.
a. Investigate and describe the magnetic fields surrounding various types of magnets using materials, such as iron filings and small compasses.
* A single bar magnet
* Two bar magnets with like poles facing
* Two bar magnets with opposite poles facing
* A horseshoe magnet
b. Explain ways to change the strength of a simple electromagnet by varying the number of coils wrapped, the amount of electricity in the wire, the number of batteries used, and whether or not an iron core is used.
c. Describe how the electromagnet demonstrates the relationship of magnetism and electricity and identify common devices that demonstrate application of this relationship.
* Electric motors (fans, hair dryers, can openers)
* Electrical generators (turbine)
d. Describe that electricity moving through a wire produces a magnetic force on materials placed near the wire.
* Iron filings
1st Big Assignment+ Please look up these
Vocabulary Words to look up and put in your journal
Electricity
Electric current
Atom
Electron
Proton
Neutron
Charge
Voltage
Electric circuit
Insulator
Conductor
Magnet
Electromagnet
Alternative current
Direct current
Electromagnetic induction
PRE TEST
PRE TEST
|
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
|
 |
|
| ||||
|
|
Please read this article and complete the work below in your journal
What Is Electricity? By Brandi Waters |  |
 1 Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers work. It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?
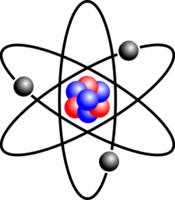
1 Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers work. It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?2 First, you have to know about atoms. All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them without a special microscope. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons both have an electrical charge. Protons have a positive charge. Electrons have a negative charge. Neutrons do not have a positive or a negative charge. Most atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the nucleus of the atom. The nucleus is at the center of an atom. Electrons circle around the nucleus like the planets orbit the sun.
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there
3 Scientists have learned that electrons can move from one atom to another. This creates electricity. You can see electricity in many forms. Lightning is a form of electricity. When you pull a sweater over your hair or rub your feet on the carpet you create static electricity. Electricity can also be made by man. This is how we get electricity to use at our houses. There are many ways that it can be made. It can be made using energy from water flowing down at a dam. It can be made by using the power of the wind. It can also be made by burning fuel. After electricity has been made, it can be moved to other places. A wire is a way of moving electricity. Electrons move from atom to atom along the wire. This creates a current of electricity. Wires run from electrical power plants to homes, schools, and businesses. The wires carry electricity to power our lights and many of our electronic devices.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there

Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there

Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
_ |
 |
 |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| 1. | Scientist uses atomic mass units to find the (Direct Current, proton, Alternative current) of a mass. | |
| 2. | Heat and friction can force some electrons to leave one (atom, Insulator, Electric current) and move to another. | |
| 3. | The force of the (Electromagnet induction, magnet, Electron) caused the paperclip to stick. | |
| 4. | (Neutron, Electron, Electricity) bills show how many killowatt-hours a house has used. | |
| 5. | An insulator is a material through which (Insulator, Magnet, electricity) connot travel. | |
| 6. | Water in a dam turns the turbines that causes the production of (Magnet, electricity, Atom) . | |
| 7. | There are power lines above our house to control the (electricity, Alternative current, induction) . | |
| 8. | A negatively charged rubber rod can pick up tiny pieces of paper by (Conductor, induction, Proton) . | |
| 9. | An (Conductor, insulator, Electricity) is used to surround an electric wire. | |
| 10. | A (Alternative current, Neutron, electron) has a negative electric charge. | |
| 11. | An (Conductor, electron, Electromagnet) has a negative electrical charge. | |
| 12. | Induced magnetism occurs when an object like, a nail is stuck to a (magnet, Voltage, Electric current) .. |
Please copy this "cloze" assignment in your journal and complete it there
What Is Electricity? By Brandi Waters |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers (1) _______________________ . It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?
Electricity is a big part of our lives. It powers our lights. It can heat and cool our homes. It can make our televisions and computers (1) _______________________ . It can even power our cars! We all use electricity every day, but what is it?First, you have to know about atoms. All (2) _______________________ is made of atoms. Atoms are very small. They are so small that you cannot see them without a special microscope. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and electrons (3) _______________________ have an electrical charge. Protons have a positive charge. Electrons have a (4) _______________________ (5) _______________________ . Neutrons do not have a positive or a negative charge. Most atoms have the same number of protons and electrons. Protons and neutrons form the nucleus of the atom. The nucleus is at the center of an atom. Electrons circle around the nucleus like the planets orbit the sun.
Scientists have learned that electrons can move from one atom to (6) _______________________ . This creates electricity. You can see electricity in many forms. Lightning is a form of electricity. When you pull a sweater (7) _______________________ your hair or rub your feet on the carpet you create static electricity. Electricity can also be made by man. This is how we get electricity to use at our houses. There are many ways that it can be made. It can be made using energy from water flowing down at a dam. It can be made by using the power of the wind. It can also be made by burning (8) _______________________ . (9) _______________________ electricity has been made, it can be(10) _______________________ to other places. A wire is a way of (11) _______________________ electricity. Electrons(12) _______________________ from atom to atom (13) _______________________ the wire. This creates a(14) _______________________ of electricity. Wires run from (15) _______________________ power plants to homes,(16) _______________________ , and businesses. The wires carry electricity to power our lights and many of our(17) _______________________ devices.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
|
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| 17. | An ____ that emits alpha particles loses protons and neurons. | |
| 18. | Turn off the current and the ____ will release the steel ball. | |
| 19. | An ____ with a negative charge will discharge its extra electrons and become neutral. | |
| 20. | My hair was full of static ____ after I brushed it . | |
| 21. | An ____ will only work if electricity is moving through the coils of wire. | |
| 22. | The elements had to exchange a ____ to be balanced. | |
| 23. | The ____ transport chain carries ATP to help produce glucose and oxygen. | |
| 24. | Atoms are so small that if you took a tiny piece of dust and cut it into a million pieces it would still be bigger than an ____. | |
| 25. | During a discharge, static ____ is changed to current electricity. | |
| 26. | The force of the ____ caused the paperclip to stick. | |
| 27. | An MRI machine uses an ____. | |
| 28. | An ____ uses electric current and creates motors. | |
| 29. | Plastic is a good ____ because it does not conduct an electric current. | |
| 30. | The force of the ____ allowed us to pick up metal objects. |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| 31. | Protons and electrons orbit around the nucleus of an ____. | |
| 32. | The ____ around the door stopped the cold air from entering the house. | |
| 33. | The two particles that make up the nucleus of an atom are the proton and the ____. | |
| 34. | In the colonial days, a turbine was used to generate ____. | |
| 35. | A ____ has a negative electrical charge. | |
| 36. | An ____ has a negative electrical charge. | |
| 37. | The rent is $300 plus ____. | |
| 38. | Water is a compound made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen ____. | |
| 39. | If you put iron filings on glass above a ____ you can see the magnetic field. | |
| 40. | Electrons, protons and neutrons are all part of the ____. | |
| 41. | A generator changes mechanical or heat energy into ____. | |
| 42. | The paper clip moved across the desk because of the force of the large ____. | |
| 43. | Scientists use ____ microscopes to study microbes. | |
| 44. | A negatively charged rubber rod can pick up tiny pieces of paper by ____. | |
| 45. | An ____ is a temporary magnet. |
Electrical Circuits By Brandi Waters |  |
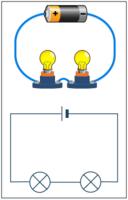 1 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons moving from atom to atom. Electrons have a negative charge. They move toward atoms with a positive charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.
1 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons moving from atom to atom. Electrons have a negative charge. They move toward atoms with a positive charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
2 Electrons cannot jump across a distance. There must be a path for electrons to follow. The path must be a series of atoms that can accept an electron. We call this path a circuit. People have learned how to build and manipulate circuits to move electricity. We use circuits to bring electricity into our homes. We use circuits to move electricity through our computers, telephones, toys, and even our cars.
Please copy this main idea and details graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| 13. | Member of the element family that has 1 valance (induction, Proton, electron) and are very reactive. They are soft, silvery - white and shiny | |
| 14. | Light energy is used to (Atom, charge, Neutron) solar panels. | |
| 15. | The charge of a proton is equal to that of an (Magnet, electron, Neutron) . | |
| 16. | A nuclear reactor uses radioactive fuel to create (electricity, Electromagnet, Conductor) . | |
| 17. | (Electric current, Electricity, Alternative current) is transmitted from the battery to the engine through cables. | |
| 18. | Atoms are so small that if you took a tiny piece of dust and cut it into a million pieces it would still be bigger than an (Direct Current, atom, Electricity) . | |
| 19. | An (Alternative current, electromagnet, Direct Current) will only work if electricity is moving through the coils of wire. | |
| 20. | We discovered that a tighter coil on a rivet will produce a stronger (Magnet, induction, electromagnet) . | |
| 21. | An electric wire needs an (insulator, Electromagnet, Voltage) wrapped around it. | |
| 22. | When Ms. Graves rubbed the balloon on Ariana's hair, the static (Electromagnet induction, Conductor, electricity) made Ariana's hair stand straight up. | |
| 23. | He used a (Insulator, magnet, Electric current) to pick up tiny pieces of iron. | |
| 24. | An (Conductor, electron, Charge) has a negative charge. |
3 Every time you flip a light switch in your house, you are using a circuit. The light bulb glows when electrons are flowing through it. The light bulb only glows when the switch is on. This is because the circuit is complete when the switch is on. Wiring in your house forms a path for electricity to flow. The wires are attached to the light bulb. The wires are also connected to the switch on the wall. When the switch is turned off, there is a break in the circuit. When the circuit is broken, electricity cannot flow through the light bulb. When the switch is turned on, the switch forms a bridge that completes the circuit. Electrons can flow through the wires, through the switch, and through the light bulb. The light bulb glows and lights your room. Circuits help people control when and where electricity flows.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Copyright © 2011 edHelper

 |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
Please click this site below , hit enter, complete the electrical circuit reading and activity.
NOW take 15 or more notes about what you learned from the reading and activity.
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| 46. | Make a prediction of whether each item is a conductor or ____. | |
| 47. | The two particles that make up the nucleus of an ____ are the proton and the neutron. | |
| 48. | An atom that has lost or gained an ____ is called an ion. | |
| 49. | We need a ____ for the wire. | |
| 50. | A electron has a negative electrical ____. | |
| 51. | The ____ cloud is suspect. | |
| 52. | Ben was astonished to see ____ in action. | |
| 53. | The ____ transport chain phase separates the light reaction from the dark reaction as food is being made in plants. | |
| 54. | Scientists penetrated the secrets of the ____. | |
| 55. | The subatomic particles are smaller than the ____. | |
| 56. | Hybrid cars use a combination of ____ and gasoline to propel them. | |
| 57. | The shell of the atom is made by the movement of an ____. | |
| 58. | An ____ is formed when electricity is put through a coil of wire. | |
| 59. | When Ms. Graves rubbed the balloon on Ariana's hair, the static ____ made Ariana's hair stand straight up. | |
| 60. | The ____ has a positive electrical charge and resides in the nucleus. |
 |
Electricity
magnetic field parallel circuit electric field
electromagnet fuse conductor
direct current voltage alternating current
insulator electricity kilowatt-hour
circuit lodestone ground
generator short circuit series circuit
resistor compass ampere
charge magnet static electricity
lightning rod
Matching
Assignment-In your journal. Match each definition with a word above
1. An electric current flowing only in one direction.
2. The amount of energy used when you consume one kilo-watt of power in one
hour.
3. A piece of metal that stands at the highest point of a building and is connected to
the Earth. The purpose of the piece of metal is to ground the large amount of
electrical energy in the event of a lightning strike.
4. A machine that produces electricity by changing energy of motion into electrical
energy.
5. An electrical connection that allows electrons to be carried away in the event of a
problem.
6. A unit used to measure current.
7. A magnet created when electric current flows through a coil of wire.
8. Energy formed by the motion of protons and electrons.
9. A measure of the amount of electricity in an atom that is determined by the extra
positive or negative particles that an atom has.
10. The area around charged particles where electric forces occur.
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| 25. | A (charge, Magnet, Proton) is a burst of energy. | |
| 26. | The two particles that make up the nucleus of an atom are the proton and the (neutron, Magnet, Voltage) . | |
| 27. | The (Electricity, Alternative current, electron) cloud is suspect. | |
| 28. | Make a prediction of whether each item is a conductor or (Charge, insulator, Electromagnet induction) . | |
| 29. | We used a rivet as the core in our (Direct Current, electromagnet, Charge) . | |
| 30. | We need a (Magnet, Proton, insulator) for the wire. | |
| 31. | The two particles that make up the nucleus of an atom are the (Atom, proton, Electron) and the neutron. | |
| 32. | The (neutron, Insulator, Electricity) is the heaviest particle in the atom. | |
| 33. | A (Electromagnet induction, Conductor, proton) is a particle that does not travel out of the atom. | |
| 34. | The part of an atom that has a positive electric charge is the (Magnet, proton, Insulator) . | |
| 35. | Metal is a good conductor of (Electron, Atom, electricity) . | |
| 36. | An (atom, Charge, Direct Current) that has lost or gained an electron is called an ion. | |
| 37. | Solar energy can be converted to (Conductor, Alternative current, electricity) on both small and large scale. |
 |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
Electrical Circuits By Brandi Waters |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons(1) _______________________ from atom to atom. Electrons have a (2) _______________________ charge. They move toward atoms with a (3) _______________________ charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.
You have already learned about electricity. You know that electricity is a stream of electrons(1) _______________________ from atom to atom. Electrons have a (2) _______________________ charge. They move toward atoms with a (3) _______________________ charge. When electrons move, electricity is made.Electrons cannot jump (4) _______________________ a distance. There must be a path for electrons to follow. The path must be a (5) _______________________ of atoms that can (6) _______________________ an electron. We call this path a circuit. (7) _______________________ have learned how to (8) _______________________ and manipulate circuits to move electricity. We use circuits to (9) _______________________ electricity into our homes. We use circuits to(10) _______________________ electricity through our computers, telephones, toys, and even our cars.
Every time you flip a light switch in your house, you are using a circuit. The light bulb glows when electrons are flowing through it. The light bulb (11) _______________________ glows when the switch is on. This is because the circuit is complete when the switch is on. Wiring in your house forms a path for (12) _______________________ to flow. The wires are attached to the light bulb. The wires are also connected to the switch on the (13) _______________________ . When the switch is turned off, there is a (14) _______________________ in the circuit. When the circuit is (15) _______________________ , electricity cannot flow through the light bulb. When the switch is turned on, the switch forms a bridge that completes the circuit. Electrons can flow through the wires, through the (16) _______________________ , and through the light (17) _______________________ . The light bulb glows and lights your room. Circuits help people control when and where electricity flows.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Multiple Choice
Please copy in your journal and Select the definition that most nearly defines the given word.
11. charge
A. A measure of the amount of electricity in an atom that is determined by the extra
positive or negative particles that an atom has.
B. A hard, black, naturally magnetic rock.
12. series circuit
A. A magnet created when electric current flows through a coil of wire.
B. An electric circuit that has only one path for the current.
13. circuit
A. The area around charged particles where electric forces occur.
B. A closed path along which electricity flows.
14. magnet
A. An object with two poles that attracts iron and steel.
B. The force that pushes electricity or a current. In most homes this force is 110 volts.
15. lodestone
A. A path that allows most of the current in an electric circuit to flow around or away
from the principal elements or devices in the circuit.
B. A hard, black, naturally magnetic rock.
16. direct current
A. The amount of energy used when you consume one kilo-watt of power in one hour.
B. An electric current flowing only in one direction.
17. alternating current
A. An electric current that reverses its direction of flow at regular intervals.
B. A unit used to measure current.
18. voltage
A. An electrical connection that allows electrons to be carried away in the event of a
problem.
B. The force that pushes electricity or a current. In most homes this force is 110 volts.
19. magnetic field
A. The space around a magnet where the force of the magnet can be felt.
B. This has a magnetized needle that is attracted to the earth's north magnetic pole.
20. static electricity
A. An electric circuit that has only one path for the current.
B. A charge that stays on an object instead of flowing in a current.
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
|
PLEASE READ THIS ARTICLE AND ANSWER THE FOLLOWING ASSIGNMENTS IN YOUR JOURNAL
Electric Current By Cindy Grigg |  |
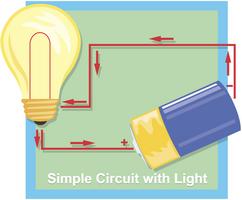 1 The electrical wires in your house make a path for the electricity to run through. Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady flow of electric charges moving from one place to another. Electric currents move in a path called a circuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do something. For example, when you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light bulb. The light comes on. Turn the light switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a small gap to turn off the light. Electric current can no longer flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the circuit. Electric current flows like water in a river bed.
1 The electrical wires in your house make a path for the electricity to run through. Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady flow of electric charges moving from one place to another. Electric currents move in a path called a circuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do something. For example, when you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light bulb. The light comes on. Turn the light switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a small gap to turn off the light. Electric current can no longer flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the circuit. Electric current flows like water in a river bed.Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Assignment=Explain in your journal what you think a GOOD title for the last paragraph of the reading could be and why?
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
_____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
|
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| 61. | Neutrons are found in the nucleus of an ____ and have no electric charge. | |
| 62. | An electron travels around the nucleus, or center, of an ____. | |
| 63. | When the ____ went off, we found ourselves in utter darkness. | |
| 64. | An ____ that has lost or gained an electron is called an ion. | |
| 65. | A telephone has an ____ in it. | |
| 66. | We used a rivet as the core in our ____. | |
| 67. | We use ____ everyday to run radios, computers and lights. | |
| 68. | A ____ has a positive electrical charge. | |
| 69. | Metal is a good conductor of ____. | |
| 70. | The ____ has no electric charge. | |
| 71. | The ____ circled the nucleus of the atom. | |
| 72. | You can make an ____ with wire, a battery, and a nail. | |
| 73. | An ____ has a negative charge. | |
| 74. | Scientist uses atomic mass units to find the ____ of a mass. | |
| 75. | There are power lines above our house to control the ____. | |
| 76. | ____ bills show how many killowatt-hours a house has used. |
Electric Current
Please click this site below , hit enter, click the 2nd of 5 pictures, complete the electrical conductors and insulators reading and activity.
NOW take 15 or more notes about what you learned from the reading and activity.
 |
Please copy this "cloze" assignment in your journal and complete it there
Electric Current By Cindy Grigg |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 The electrical wires in your house (1) _______________________ a path for the electricity to run(2) _______________________ . Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady(3) _______________________ of electric charges moving from one place to(4) _______________________ . Electric currents move in a (5) _______________________ called acircuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do(6) _______________________ . For example, (7) _______________________ you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light(8) _______________________ . The light comes on. Turn the (9) _______________________ switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a (10) _______________________ gap to (11) _______________________ off the light. Electric current can no (12) _______________________ flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the (13) _______________________ . Electric current (14) _______________________ like(15) _______________________ in a (16) _______________________ bed.
The electrical wires in your house (1) _______________________ a path for the electricity to run(2) _______________________ . Electricity is also called electric current. Electric current is a steady(3) _______________________ of electric charges moving from one place to(4) _______________________ . Electric currents move in a (5) _______________________ called acircuit. If the circuit is complete, or unbroken, then the electric current can be used to do(6) _______________________ . For example, (7) _______________________ you turn on a light switch in your house, you complete the circuit. Electric current can flow through the wires of the house to the light(8) _______________________ . The light comes on. Turn the (9) _______________________ switch off. The electric circuit is not complete any more. The switch opens a (10) _______________________ gap to (11) _______________________ off the light. Electric current can no (12) _______________________ flow through the wires to the light bulb. A switch opens or closes the (13) _______________________ . Electric current (14) _______________________ like(15) _______________________ in a (16) _______________________ bed.Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| __________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| 38. | A (Insulator, electron, Voltage) has a negative electrical charge. | |
| 39. | If a computer disk gets to close to a (magnet, Proton, Direct Current) it may delete you files. | |
| 40. | If you put iron filings on glass above a (magnet, Voltage, Neutron) you can see the magnetic field. | |
| 41. | If you split the nucleus of an (atom, Electromagnet, Magnet) , it will release energy. | |
| 42. | A good electrical (insulator, Electromagnet, Charge) is rubber. | |
| 43. | The (Voltage, Magnet, neutron) has a neutral charge. | |
| 44. | The paper clip moved across the desk because of the force of the large (magnet, Electricity, Electromagnet induction) . | |
| 45. | A (magnet, Alternative current, Atom) can be in the szhape of a bar, a ring or a horseshoe. | |
| 46. | Rubber is a good (Conductor, insulator, Electromagnet induction) . | |
| 47. | A (proton, Direct Current, Conductor) is a particle with a positive charge. | |
| 48. | A material that does not transfer charge easily is an (Neutron, insulator, Atom) . | |
| 49. | An (electromagnet, Magnet, Proton) is a temporary magnet. | |
| 50. | Styrofoam is a good (insulator, Atom, induction) . |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
 |
|
| ||||
|
|
Please click this site below , hit enter, click the 3rd of 5 pictures, complete the electrical switches reading and activity.
NOW take 15 or more notes about what you learned from the reading and activity.
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
Review
21. The magnetic force is strongest at a magnet's poles.
A. True
B. False
22. An electromagnet is a temporary magnet.
A. True
B. False
23. What is the most dangerous part of electricity?
A. The charge
B. Electricity is not dangerous at all.
C. The current
D. The voltage
24. Thomas designs an electric circuit that has 2 batteries connected in series and 1 bulb.
If one of the batteries dies, the brightness of the bulb remains the same.
A. False
B. True
25. What does a switch use to make or break an electric current?
A. Resistors only
B. Conductors and insulators
C. Conductors and resistors
D. Insulators and resistors
26. What did Benjamin Franklin invent in 1752?
A. A kite
B. A key
C. Lightning
D. A lightning rod
27. Lodestone is a natural mineral that possesses magnetic properties.
A. False
B. True
28. What is the area around charged particles where electric forces occur?
A. A power field
B. An electromagnetic field
C. A magnetic field
D. An electric field
29. Emily can control the brightness of her living room lights by turning a knob. If Emily
dims the lights, the knob increases the resistance to the electric current.
A. True
B. False
30. What good insulator material is often used to coat electrical wires?
A. Plastic
B. Paper
C. Copper
D. Aluminum
Please click this site below , hit enter, click the 4th of 5 pictures, complete the changing circuits reading and activity.
NOW take 15 or more notes about what you learned from the reading and activity.
Electricity - Circuit Construction
Electricity - ADV. circuit construction
Electricity- Signal Circuit
Electricity - Adv-Resistance in a Wire
Electricity - Ohms Law -Adv
Electric Generator
Faradays Law
Faradays Electromagnetic Lab
Electric Circuit
Electricity -
Battery-Resistor Circuit
Battery Voltage
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| 51. | The (Neutron, Electron, insulator) around the door stopped the cold air from entering the house. | |
| 52. | The (Neutron, Magnet, electron) travels in an orbit around the nucleus of an atom. | |
| 53. | The subatomic particles are smaller than the (Conductor, Alternative current, atom) . | |
| 54. | The atom receiving the (Electric current, electron, Proton) becomes negative in charge. | |
| 55. | Protons and electrons orbit around the nucleus of an (Electromagnet induction, atom, Electricity) . | |
| 56. | An MRI machine uses an (electromagnet, Insulator, Voltage) . | |
| 57. | THE (Electromagnet induction, ATOM, Alternative current) IS SMALLER THAN A CELL, OR A MOLECULE. | |
| 58. | The neutron is in the nucleus of the (induction, Electromagnet, atom) . | |
| 59. | The (neutron, Electricity, Electric current) has no electrical charge. | |
| 60. | The (charge, Electron, Direct Current) of a proton is equal to that of an electron. | |
| 61. | An (atom, Direct Current, Proton) that emits alpha particles loses protons and neurons. | |
| 62. | A telephone has an (Electric current, electromagnet, Atom) in it. | |
| 63. | A (Direct Current, proton, Neutron) has a positive charge. |
ELECTROMAGNETISM
| Producing and Supplying Electricity: Garden of Amps |  |
 1 Most plants grow in pots or in gardens. However, some plants are made from steel and concrete. These plants, electrical power plants, are very important to the millions of people around the world who depend on electricity each day. The seeds for electricity production were planted during the 1800s. In 1819 a Danish scientist named Hans Christian Oersted discovered by accident that electricity and magnetism were connected. Oersted was demonstrating how electrical currents could produce heat when he noticed a strange sight. There was a compass on a nearby table, and when the wires were connected in his circuit to the power source, the needle on the compass swung around. When he disconnected the wires, the compass needle returned to its normal position pointing towards the magnetic north pole. Electricity had magnetic pull!
1 Most plants grow in pots or in gardens. However, some plants are made from steel and concrete. These plants, electrical power plants, are very important to the millions of people around the world who depend on electricity each day. The seeds for electricity production were planted during the 1800s. In 1819 a Danish scientist named Hans Christian Oersted discovered by accident that electricity and magnetism were connected. Oersted was demonstrating how electrical currents could produce heat when he noticed a strange sight. There was a compass on a nearby table, and when the wires were connected in his circuit to the power source, the needle on the compass swung around. When he disconnected the wires, the compass needle returned to its normal position pointing towards the magnetic north pole. Electricity had magnetic pull!Please copy this graphic organizer in your journal and complete it therefrom the paragraph above
 |
| Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer |
2 In 1820, French scientist André Ampere proved that parallel wires carrying electric currents in the same direction in a circuit would attract each other like unlike poles on the ends of bar magnets. If the current flowed in opposite directions, the wires would repel each other. Ampere used his observations to make a cylindrical (circular) coil of wire that behaved like a magnet. Today we call cylindrical coils of wire solenoids.
Please copy this graphic organizer in your journal and complete it therefrom the paragraph above
 |
| Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer |
Assignment= In your journal, explain what a solenoid is
3 In 1825, William Sturgeon, an English scientist discovered that you could increase the power of an electromagnet (combination of electricity and magnets) by placing a bar of soft iron inside a coil of wire. In 1831, American Joseph Henry made improvements to Sturgeon's electromagnet by insulating or wrapping the wires to help hold in the heat from the electrical current. This helped to increase the power of the electromagnet. During that same year, Henry helped to develop an electromagnet that was capable of lifting over a ton (2000 pounds).
Please copy this graphic organizer in your journal and complete it therefrom the paragraph above
 |
| Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer |
Assignment= In your journal, explain what a "magnetic field" is.
Please copy this graphic organizer in your journal and complete it therefrom the paragraph above
 |
| Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer |
5 During the 1830s, Faraday experimented with creating electrical currents by using magnets. His experiment included two coils of wires lying next to each other. One coil of wire had an iron bar inside to make it a stronger magnet. When Faraday sent a current through the coil with the iron bar, he had hoped to create an electrical current in the second coil. What he really saw was a small burst of electricity in the second coil and the end of that experiment. He then realized that he needed to move the wire across the magnetic field to produce the current. Faraday tried the experiment again. He moved the iron bar in and out of the coil and moved the loop of wire across the magnetic field. Each time Faraday did this, he caused an electric current to be induced or made in the second coil. Faraday proved that the movement of magnets and wires within a magnetic field produced electricity. Thus, Faraday planted the ultimate seed, the theory of electromagnetic induction. This meant that electricity could be produced, possibly in large quantities. Around this time Joseph Henry also made the same discovery.
Please copy this graphic organizer in your journal and complete it therefrom the paragraph above
 |
| Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer |
Please copy this graphic organizer in your journal and complete it therefrom the paragraph above
 |
| Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer |
Assignment= In your journal, explain what a "dynamo" is.
Please copy this graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above
 |
| Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer |
9 The answer is through power lines. Once the electricity is produced, it is transferred from the power plant or station through a series of cables or grid. When electricity is sent from the power station, it measures about 25,000 volts or more. As the electricity travels along the power lines, it passes through transformers. Transformers are like boxes that take in the electricity at a certain voltage on one side and increase or decrease the voltage as it passes through the other side. When the electricity leaves the power plant, the transformers increase the voltage (up to 400,000 volts) because less energy will be lost due to the resistance in the cables. As the electricity is transferred to homes and businesses, the voltage is increased or decreased. The voltages for businesses, factories, and homes are usually 110 to 240 volts and can vary in different countries.
Assignment=Please explain in your journal what a "transformer" is concerning electricity.
Please copy this SEQUENCE graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above
Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Company. All Rights Reserved.
Topic= How Does Electricity Travel To Our Homes?
First=
Next=
Next=
Next=
Last=
11 Our methods for producing electricity today come from the extraordinary work of scientists in the 1800s. Without their hard work and cultivation, the seeds for electromagnetism would never have been planted.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| ____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| 77. | THE ____ IS SMALLER THAN A CELL, OR A MOLECULE. | |
| 78. | Two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen ____ bond to form water. | |
| 79. | Water in a dam turns the turbines that causes the production of ____. | |
| 80. | The ____ has no electrical charge. | |
| 81. | Protons have a positive ____ and are in the nucleus of the atom. | |
| 82. | A crane with an ____ can pick up a car. | |
| 83. | The nail when rubbed my the ____ became induced. | |
| 84. | The class built an ____. | |
| 85. | The ____ we use is generated by huge power plants. | |
| 86. | The two particles that make up the nucleus of an atom are the ____ and the neutron. | |
| 87. | A small spark of static ____ shocked my cat when I brushed her coat. | |
| 88. | The source of ____ was the sun. | |
| 89. | A ____ has a positive charge. | |
| 90. | Gold is a good conductor of electricity and not an ____. | |
| 91. | The south pole of one ____ attracts the north pole of another magnet. | |
| 92. | The north pole of a ____ is attracted to the south pole of another magnet. |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| ___________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| 64. | The (Electric current, Charge, neutron) is in the nucleus of the atom. | |
| 65. | Turn off the current and the (Neutron, induction, magnet) will release the steel ball. | |
| 66. | A (proton, Electricity, Charge) has a positive electrical charge. | |
| 67. | An (electromagnet, Electromagnet induction, Conductor) uses electric current and creates motors. | |
| 68. | A small spark of static (Conductor, electricity, Electric current) shocked my cat when I brushed her coat. | |
| 69. | The electrical cooperative pooled their money in order to provide (Alternative current, electricity, Voltage) to the Nile River valley. | |
| 70. | During a discharge, static (electricity, Electron, Electric current) is changed to current electricity. | |
| 71. | Analyze how a windmill creates (Direct Current, Charge, electricity) . | |
| 72. | There are three basic types of (Proton, Charge, electron) microscopes. | |
| 73. | When the (Charge, Proton, electricity) went off, we found ourselves in utter darkness. | |
| 74. | Metal is a good medium through which to transmit (electricity, Direct Current, Charge) . | |
| 75. | An (Conductor, insulator, Voltage) on the outside of a wire stops the electricity and keeps you from getting shocked. |
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
Please copy this "cloze"assignment in your journal and complete it there
| Producing and Supplying Electricity: Garden of Amps |  |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Most plants grow in pots or in gardens. However, some plants are made from steel and concrete. These plants, electrical power plants, are very important to the millions of people around the world who depend on electricity each day. The seeds for electricity production were planted during the 1800s. In 1819 a Danish scientist named Hans Christian Oersted discovered by accident that electricity and(1) _______________________ were connected. Oersted was demonstrating how electrical currents could produce heat when he noticed a strange sight. There was a compass on a nearby table, and when the wires were connected in his circuit to the power source, the needle on the compass swung around. When he disconnected the wires, the (2) _______________________ needle returned to its normal position pointing towards the magnetic north pole. Electricity had magnetic pull!
Most plants grow in pots or in gardens. However, some plants are made from steel and concrete. These plants, electrical power plants, are very important to the millions of people around the world who depend on electricity each day. The seeds for electricity production were planted during the 1800s. In 1819 a Danish scientist named Hans Christian Oersted discovered by accident that electricity and(1) _______________________ were connected. Oersted was demonstrating how electrical currents could produce heat when he noticed a strange sight. There was a compass on a nearby table, and when the wires were connected in his circuit to the power source, the needle on the compass swung around. When he disconnected the wires, the (2) _______________________ needle returned to its normal position pointing towards the magnetic north pole. Electricity had magnetic pull!In 1820, French scientist André Ampere proved that parallel wires carrying electric currents in the same direction in a circuit would attract each other like unlike poles on the ends of bar magnets. If the current flowed in opposite directions, the wires would repel each other. Ampere used his observations to make a cylindrical ((3) _______________________ ) coil of wire that behaved like a magnet. Today we call cylindrical coils of wire solenoids.
In 1825, William Sturgeon, an English scientist discovered that you could increase the power of an electromagnet (combination of electricity and magnets) by placing a bar of soft iron inside a coil of wire. In 1831, American Joseph Henry made improvements to Sturgeon's electromagnet by insulating or (4) _______________________ the wires to help hold in the heat from the electrical current. This helped to increase the power of the electromagnet. During that same year, Henry helped to develop an electromagnet that was capable of lifting over a ton (2000 pounds).
The one scientist who had the greatest impact on future electricity (5) _______________________ was Englishman Michael Faraday. Faraday used two bar magnets (6) _______________________ in electrical coils and sprinkled iron filings onto a piece of paper above the two electromagnets. After the iron filings formed around the electromagnets, Faraday stated that the lines of filings on the paper marked the real lines of electromagnetic force. He is the scientist who called the area around a magnet a magnetic field. The idea of fields is a very important concept in science today.
During the 1830s, Faraday experimented with creating electrical currents by using magnets. His experiment included two coils of wires lying next to each other. One coil of wire had an iron bar inside to make it a stronger magnet. When Faraday sent a current through the coil with the iron bar, he had hoped to create an electrical current in the second coil. What he really saw was a small burst of electricity in the second coil and the end of that experiment. He then realized that he needed to move the wire across the magnetic field to produce the current. Faraday tried the experiment again. He moved the iron bar in and out of the coil and moved the loop of wire across the magnetic field. Each time Faraday did this, he caused an electric current to be induced or made in the second coil. Faraday proved that the movement of magnets and wires within a magnetic field produced electricity. (7) _______________________ , Faraday planted the ultimate seed, the theory of electromagnetic induction. This meant that electricity could be produced, (8) _______________________ in large quantities. Around this time Joseph Henry also made the same discovery.
So how does all of the hard work of these scientists help us today? Each scientist's piece of the electromagnetic puzzle helped to form the (9) _______________________ of electromagnetic induction. Oersted, Ampere, Sturgeon, Henry, and Faraday learned from the experiments of the scientists before them, and they used that knowledge to help build the parts of an extraordinary scientific theory. Today the generators in the world's power plants are built using this theory to generate electricity.
Generators are large machines built with turbines (cylinders) that have magnets which spin between coils of wires. The stronger the magnet, the faster it turns, and the more coils the machine has, the stronger the voltage or power that is created. Generators produce over 99% of our electricity. There are two types of generators. Alternators (AC) send alternating current that switches directions. As the magnets spin in the machine, they pass the wires going up on one side and down on the other side. The result is a current that changes direction. Alternators, which are the simplest form of generator, are found mostly in houses. Dynamos (DC) send direct currents in the same direction. The magnets in these machines only pass the wires in one direction on each side. Household batteries give direct electrical current.
Generators can be powered by different types of fuel. Hydroelectric power plants use moving water to turn the turbines (spinning machines) in the generators to spin the magnets around. The Aswan Dam (Egypt, Africa), the Three Gorges Dam (China), Niagara Falls (New York, U.S.A.), the Hoover Dam (Nevada-Arizona Border, U.S.A.) are the world's most famous hydroelectric power plants. Other types of power plants are geoelectric (coal and oil), geothermal (hot water from underground), solar (10) _______________________ (heat from the sun), and (11) _______________________ (energy from atoms). In these power plants, the(12) _______________________ produces the steam that makes the turbines turn and, therefore, spins the magnets to produce electricity. How does this electricity travel to our homes?
The answer is through power lines. Once the electricity is produced, it is transferred from the power plant or station through a series of cables or grid. When electricity is sent from the power station, it measures about 25,000 volts or more. As the electricity travels along the power lines, it passes through transformers. Transformers are like boxes that take in the electricity at a certain voltage on one side and increase or decrease the(13) _______________________ as it passes through the other side. When the electricity leaves the power plant, the transformers increase the voltage (up to 400,000 volts) because less energy will be lost due to the resistance in the cables. As the electricity is transferred to homes and businesses, the voltage is increased or decreased. The (14) _______________________ for businesses, factories, and homes are usually 110 to 240 volts and can vary in different countries.
There are times, however, when the circuit from the power plant to our homes is broken. Widespread power outages or (15) _______________________ can occur when you have blown or exploded transformers or(16) _______________________ power lines. In 1965 a blown transformer caused a (17) _______________________ in New York City. Hurricanes and tornadoes are notorious for causing power lines to fall down and, therefore, cause electricity to be lost in those areas.
Our methods for producing electricity today come from the extraordinary work of scientists in the 1800s. Without their hard work and (18) _______________________ , the seeds for electromagnetism would never have been planted.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| ____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
| 76. | A (magnet, Charge, Electric current) has a positive pole and a negative pole. | |
| 77. | A generator changes mechanical or heat energy into (Electromagnet, electricity, Magnet) . | |
| 78. | Ben was astonished to see (electricity, Neutron, Direct Current) in action. | |
| 79. | In the colonial days, a turbine was used to generate (Proton, electricity, Insulator) . | |
| 80. | Electrons are found outside the nucleus in the (Electromagnet induction, electron, Direct Current) cloud. | |
| 81. | Copper is an excellent metal for conducting (electricity, Neutron, Direct Current) . | |
| 82. | A plastic picnic cooler is a good (induction, insulator, Electron) . | |
| 83. | Water is a compound made of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen (atom, Electricity, Magnet) . | |
| 84. | Iron filings sprinkled over a (Electron, Electromagnet, magnet) form lines of force that show the strength and the direction of the magnet's force. | |
| 85. | The (Voltage, proton, Magnet) has a positive electrical charge and resides in the nucleus. | |
| 86. | The elements had to exchange a (neutron, Electromagnet, Atom) to be balanced. | |
| 87. | Neutrons are found in the nucleus of an (atom, Alternative current, Electron) and have no electric charge. |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| _____________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
|
|
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
| ___________________________ |  | Date ___________________ |
|
| 93. | The ____ has an atomic mass unit of 1. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 94. | Copper is an excellent metal for conducting ____. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 95. | Heat and friction can force some electrons to leave one ____ and move to another. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 96. | A ____ is a particle that does not travel out of the atom. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 97. | The ____ is the heaviest particle in the atom. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 98. | Solar energy can be converted to ____ on both small and large scale. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 99. | A ____ picks up things. Please read this article and answer the following assignments in your journal
 1 Food, air, water, and shelter. People need these to survive. The Earth provides resources for all these things. Natural resources are materials found on the Earth. They include air, water, and land. They also include rocks, minerals, and soil. Even living things are natural resources. These are the building blocks of all the things we need to live. 1 Food, air, water, and shelter. People need these to survive. The Earth provides resources for all these things. Natural resources are materials found on the Earth. They include air, water, and land. They also include rocks, minerals, and soil. Even living things are natural resources. These are the building blocks of all the things we need to live.2 Some of Earth's resources can be cycled over and over. These are called renewable resources. Others can't be replaced quickly. These are called nonrenewable resources. 4 Living things are renewable resources. People cut down trees to use for wood. They build and heat homes with it. If a tree is cut, another one can be planted in its place. In a few years, it will be as large as the one that was cut down. As it grows, it helps supply living things with oxygen, another important resource. Trees and other plants are examples of renewable resources. 5 Animals are used for food by other living things. Animals can reproduce naturally. As long as some adults of the species survive, there will be offspring. Some people raise animals for food. Cattle and chickens can be replaced in a short period of time. 6 All living things are dependent on the sun. Plants use sunlight to produce food. They, in turn, provide food for other living things. The sun provides energy for almost all processes on Earth. Thankfully, sunlight is a renewable resource. Scientists predict that the sun will still be burning for at least another five billion years. 7 Have you been to a jewelry store lately? Did you put oil in your car today? Do you know anyone who burns coal to heat his home? If so, you have seen examples of nonrenewable resources. These substances exist in fixed amounts. They cannot be replaced quickly. 8 Diamonds are an example of a nonrenewable resource. These beautiful gems are worn and adored by many people. Do you know how diamonds are formed? Carbon must undergo tremendous pressure for millions of years. As you can see, they cannot be replaced quickly! Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.  Food, air, water, and shelter. People need these to survive. The Earth (1) _______________________ resources for all these things. (2) _______________________ resources are materials found on the Earth. They include air, water, and land. They also include rocks, minerals, and (3) _______________________ . Even living things are natural resources. These are the building blocks of all the things we need to live. Food, air, water, and shelter. People need these to survive. The Earth (1) _______________________ resources for all these things. (2) _______________________ resources are materials found on the Earth. They include air, water, and land. They also include rocks, minerals, and (3) _______________________ . Even living things are natural resources. These are the building blocks of all the things we need to live.Some of Earth's resources can be cycled over and over. These are called renewable resources. Others can't be replaced quickly. These are called nonrenewable resources. Renewable resources can be used and replaced over and over again. Using them will not (4) _______________________ the supply that is available. Examples of renewable natural resources are fresh air, water, and soil. These materials are replaced by nature at a (5) _______________________ fast rate. Living things are renewable resources. People cut down trees to use for wood. They build and heat homes with it. If a tree is cut, another one can be planted in its place. In a few years, it will be as large as the one that was cut down. As it grows, it helps supply living things with oxygen, another important (6) _______________________ . Trees and other plants are (7) _______________________ of renewable resources. Animals are used for food by other living things. Animals can (8) _______________________ naturally. As long as some adults of the species survive, there will be (9) _______________________ . Some people raise animals for food. Cattle and chickens can be replaced in a short period of time. All living things are dependent on the sun. Plants use sunlight to produce food. They, in turn, (10) _______________________ food for other living things. The sun provides energy for almost all processes on Earth. Thankfully, sunlight is a renewable resource. Scientists predict that the sun will still be (11) _______________________ for at least another five billion years. Have you been to a jewelry store lately? Did you put oil in your car today? Do you know anyone who (12) _______________________ coal to heat his home? If so, you have seen examples of (13) _______________________ resources. These substances (14) _______________________ in fixed amounts. They cannot be replaced quickly. Diamonds are an (15) _______________________ of a nonrenewable resource. These beautiful gems are worn and adored by many people. Do you know how diamonds are formed? Carbon must undergo(16) _______________________ pressure for millions of years. As you can see, they cannot be replaced quickly! Other examples of nonrenewable resources that are used for jewelry include (17) _______________________ , silver, and gold. These metals are mined underground. They are in limited supply. When the mines run out, there will be no more of these metals available naturally. Coal and oil deposits beneath the Earth formed millions of years ago. These resources are the result of the (18) _______________________ of certain plants and animals. They are also examples of nonrenewable resources. They are being used up much faster than they can be replaced. Someday, the Earth will run out of these precious materials. Natural (19) _______________________ are necessary for life on Earth. Some cannot be replaced. We need to protect them. Reduce, reuse, and recycle! Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Energy SourcesNonrenewableEnergy sources are of two types: nonrenewable and renewable. Energy sources are considered nonrenewable if they cannot be replenished (made again) in a short period of time. On the other hand, renewable energy sources such as solar and wind can be replenished naturally. Nonrenewable BasicsThe four nonrenewable energy sources used most often are:
Nonrenewable energy sources come out of the ground as liquids, gases, and solids. Crude oil (petroleum) is the only commercial nonrenewable fuel that is naturally in liquid form. Natural gas and propane are normally gases, and coal is a solid. Fossil Fuels Are Nonrenewable, but Not All Nonrenewable Energy Sources Are Fossil FuelsCoal, petroleum, natural gas, and propane are all considered fossil fuels because they were formed from the buried remains of plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. Uranium ore, a solid, is mined and converted to a fuel used at nuclear power plants. Uranium is not a fossil fuel, but is a nonrenewable fuel. |
Please copy this graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading above about nonrenewable resources
 |
| Main Idea and Details Graphic Organizer |
Examples of another 5 Renewable Resources are:
Wave Energy: Produce electricity from the power of waves.
Tidal Energy: Traps water in dams to supply to hydropower generators.
Thermal energy conversion: Use solar-heated surface water to produce electricity.
POST TEST
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
|





No comments:
Post a Comment