1.6-8.A Constructing Knowledge 1. Design, analyze or carry out simple investigations and formulate appropriate conclusions based on the data obtained or provided. 1.6-8.B. Applying Evidence and Reasoning 1. Review data from a simple experiment, summarize the data, and construct a logical argument about the cause-and-effect relationships in the experiment. 1.6-8.C Communicating Scientific Information 1. Develop explanations that explicitly link data from investigations conducted, selected readings and when appropriate, contributions from historical discoveries. 1. Analyze the value and the limitations of different types of models in explaining real things and processes.
|
· Organisms possess structures and behaviors, which indicate their relatedness. | |
| |
· Living things grow, use food, reproduce, and respond to their surroundings. · Biologists use a classification system to organize living things into groups by shared characteristics. · Animals and plants can be grouped by observable features and can be placed in different groups. · Some organisms consist of only a single cell, while others are multicellular. · Living things are made of cells. · Cells vary greatly in appearance and perform very different roles in the organism · Some organisms have characteristics that make them better suited to certain environments. 1st BIG assignment = Please look up these vocabulary words and put the words and their definitions into your journal. Please read this article and answer the questions in your journal There are many different things living on Earth. Living things have a variety of traits and characteristics. Some living things cannot move at all. Other things have wings, fins, or legs. Some are large, and others are quite small. Scientists call all living things organisms. But scientists needed to separate all of these organisms into different groups in order to study them.
Please read this article and answer the questions in your journal |
|
Scientists use classification to learn more about the multitude of organisms on Earth. Scientists put these living things into different groups. These groups are based on the characteristics that the organisms share. The characteristics of one group are different than the characteristics of another group. One example of the way animals are grouped is what they look like. For example, an organism may be covered in feathers or fur. It may have flowers or broad leaves etc. Physical features help scientists to put the organisms in different classifications or groups. Assignment= Context Clues: Please explain in your journal what do you think "multitude" means in the previous paragraph?
Assignment= Context Clues: Please explain in your journal what do you think "physical features" means in the previous paragraph? Assignment= Please copy this question and it's possible answers in your journal and answer this question from the reading. "Why do you think scientists classify horses and zebras in the same group?" a) They eat similar foods. b) They run at similar speeds c) They have similar predators that eat them d) They have similar physical features
Please read this article and answer the questions in your journal |
|
What makes a living thing a plant? All plants have the following characteristics: 1. Plants make their own food. 2. Plants cannot move from place to place. 3. Plant cells have structures called "cell walls". Although all plants share their traits, some plants share more characteristics with one another than with other plants. Scientists separate plants into 2 main groups based on their characteristics. They classify the plant as being vascular or being nonvascular.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying plants |
|
|
|
Vascular plants have leaves, stems and roots. Their roots, stems and leaves contain tubes made up of vascular tissue that carries water and nutrients throughout the plant. These tube are very, very small. But the plants can grow very tall because of these tubes. Bushes, trees, and grass are examples of vascular plants. Nonvascular plants do not have true roots, stems and leaves. They also do not have many vascular tissues. They cannot move water and nutrients great distances, so they are usually smaller plants. Mosses, and liverwort are examples of nonvascular plants.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying 2 kinds of plants |
|
|
|
Please read this article and answer the questions in your journal |
|
What makes an organism an animal? All animals have the following 3 characteristics: 1) Animals cannot make their own food. 2) Animals can move from place to place. 3) Animal cells do not have cell walls. Scientist classify animals into 2 main groups: vertebrates and invertebrates. Vertebrates have a hard, bumpy backbone that holds the body up. Invertebrates do not have a backbone.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying animals |
|
|
|
 There are several main groups of vertebrate animals. They are birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. There are several main groups of vertebrate animals. They are birds, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
Invertebrate animals include animals such as insects, spiders, snails, crabs, jellyfish, squid and worms.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ classifying 2 kinds of animals |
|
|
|
Assignment= Please explain in your journal how tigers and worms are both animals. Which of these 4 characteristics do they both have? a. They both have cells with cell walls. b. They both make their own food. c. They both have back bones. d. They both can move around. People once thought that everything alive on earth was either a plant or an animal. Over time, scientists gained new knowledge about living things and discovered new organisms. They realized that not all living things fit the characteristics of plants or animals. One such example is that of the mushroom. Mushrooms cannot make their own food, and they cannot move. Since they cannot make their own food, they are not plants. Since they cannot move around, they are not animals. The scientists had to make a new group for them. They are now part of the "fungi" group. The fungus organism is also a part of the same group. Other new groups like bacteria and slime molds also have their own groups that are not connected to plants or animals. The classification of organisms helps scientists determine how related different organisms are to each other. Relatedness is a word scientists use to explain how much or how little two organisms have in common. Living beings in the same group have characteristics in common. They are more closely related to each other than they are to organisms in other groups. Scientists separate different organisms within the same group into smaller groups based on their characteristics. The smaller the group., the more closely related its members are. For example, human beings belong to a group of vertebrate animals called mammals. Some other animals in this group are dolphins, bears, rats, and apes. Another example is with frogs, worms and snails. They are all animals. They are more closely related to each other than they are to ANY plant. Yet, worms and snails are invertebrates, and frogs are vertebrates. This also means that worms and snails are more closely related to each other than they are to frogs. Scientists classify all 3 living things into a large group - animals; however, they classify worms and snails as invertebrates, and frogs as vertebrates.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ relatedness and smaller groups of classifying |
|
|
|
In some situations, plants or animals look very similar when they are not very closely related. For example, birds, bats, and bees all can fly with wings. Yet, bees have no backbones so they are different than the vertebrate birds and bats. The scientists have to take the classification system even further with these 3 flying animals. Birds and bats both are vertebrates, but scientists put them in different groups because they have different characteristics. They are:bats five birth to their young and have fur, and birds lay eggs and have feathers. Vertebrates (birds and bats)
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the reading @ relatedness and smaller groups of classifying |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Main Idea and Details
Mammals, reptiles, birds, amphibians and fish all have something in common - they all have a backbone. Here are the basics on each group. |
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
|

1 When we go to a bookstore, we see thousands of books neatly arranged first by subjects (such as novels, memoirs, comics, and history) and then by the alphabetical order of authors' last names. Since all the books are put away in a methodical order, it is easy for us to look up a book that we are interested in.
2 Scientists use a similar approach to categorize all the animals that have ever lived on Earth. By observing each animal's bodies and behaviors, scientists are able to identify animals with similar traits and group them together. From there, scientists make further distinctions or separations among animals of a given group and break the group into many smaller groups. Scientists continue this process until they can dissect or split up the group no more.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
Assignment=CONTEXT CLUES - Please explain in your journal what the word"dissect" means in the paragraph above.
3 If we are to draw out a diagram to demonstrate scientists' methodology, we will construct a multi-level classification system. The rule of thumb is this: the higher a level is in the animal classification scheme, the more animals it has. Let's look at the table below to see how many levels the animal classification system has and how scientists classify giraffes.
4
Levels (from the highest to the lowest) | Example |
Kingdom | Kingdom Animalia is the broadest category of all in the animal classification system. It includes every animal. |
Phylum (plural: Phyla) | Phylum Chordata includes all animals of the Kingdom Animalia that have spinal cords. |
Class | Class Mammalia includes all warm-blooded animals of the Phylum Chordata that have hair and feed their young with milk. |
Order | Order Artiodactyla includes all animals of the Class Mammalia that have an even number of toes in their hooves. |
Family | Family Giraffidae includes all animals of the Order Artiodactyla that have long legs, a long narrow head with small horns, thin lips, and long tongues. |
Genus (plural: Genera) | Genus Okapia and Genus Giraffa |
Species | Species camelopardalis, also known as giraffes in English. |
5 As you go through the example above, you may have a hard time pronouncing some of the words (such as Animalia and Artiodactyla). Well, just in case you wonder if you are reading English, you really are not! These words, in either Greek or Latin, are the scientific names that scientists use in their animal classification system. Why do they give animals scientific names? Well, with over 6,000 languages in the world, scientists from any two countries may name the same animal differently. For instance, while we are very excited to see "giraffes", children in China are very excited to see "long neck deer". To avoid confusion, scientists all over the world use animals' scientific names. Hence, in the case of giraffes, scientists from both China and the United States call them Giraffa camelopardalis. The first part of the name is giraffes' genus name, and it always begins with a capital letter. The second part of the name is giraffes' species name, and it always begins with a lower case letter.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer
|
Assignment=CONTEXT CLUES - Please explain in your journal what the word"genus name" means in the paragraph above.
6 The history of the animal classification system can be traced back to the 18th century. Carl von Linné, a Swedish botanist, established taxonomy, the science of identifying, classifying, and naming all the organisms. He even gave himself a scientific name: Carolus Linnaeus!
7 Due to his hard work as well as other taxonomists' painstaking efforts, we have a well-structured classification system for not only animals, but also other living things on Earth.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Animal Classification
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ (Key 1 - Answer ID # 0473888) |
Assignment= In your journal, please write a paragraph using all of the words that are given.
1. | | classification, confusion, identify, lived, taxonomy |
|
2. | | identify, spinal, novels, narrow |
|
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
When we go to a bookstore, we see thousands of books neatly arranged first by subjects (such as novels, memoirs, comics, and history) and then by the alphabetical order of authors' last names. Since all the books are put away in a (1) _______________________ order, it is easy for us to look up a book that we are interested in.
Scientists use a similar approach to categorize all the animals that have ever lived on Earth. By observing each animal's (2) _______________________ and behaviors, scientists are able to (3) _______________________ animals with comparable traits and group them together. From there, scientists make further distinctions among animals of a given group and break the group into many smaller groups. Scientists continue this process until they can dissect the group no more.
If we are to draw out a diagram to demonstrate scientists' (4) _______________________ , we will construct a (5) _______________________ classification system. The rule of thumb is this: the higher a level is in the animal classification scheme, the more animals it has. Let's look at the table below to see how many levels the animal classification system has and how scientists (6) _______________________ giraffes.
Levels (from the highest to the (7) _______________________ ) | Example |
Kingdom | Kingdom Animalia is the broadest category of all in the animal (8) _______________________ system. It includes every animal. |
Phylum (plural: Phyla) | Phylum Chordata includes all animals of the Kingdom Animalia that have spinal cords. |
Class | Class Mammalia includes all (9) _______________________ animals of the Phylum Chordata that have hair and feed their young with milk. |
Order | Order Artiodactyla includes all animals of the Class Mammalia that have an even number of toes in their hooves. |
Family | Family Giraffidae includes all animals of the Order Artiodactyla that have long legs, a long narrow head with small horns, thin lips, and long tongues. |
Genus (plural: Genera) | Genus Okapia and Genus Giraffa |
Species | Species camelopardalis, also known as giraffes in English. |
As you go through the example above, you may have a hard time pronouncing some of the words ((10) _______________________ as Animalia and Artiodactyla). Well, just in case you wonder if you are reading English, you really are not! These words, in either Greek or Latin, are the scientific names that scientists use in their animal classification system. Why do they give animals scientific names? Well, with over 6,000 languages in the world, scientists from any two countries may name the same animal differently. For instance, while we are very excited to see "giraffes", children in China are very excited to see "long neck deer". To avoid confusion, scientists all over the world use animals' scientific names. (11) _______________________ , in the case of giraffes, scientists from both China and the United States call them Giraffa camelopardalis. The first part of the name is giraffes' genus name, and it always begins with a capital letter. The second part of the name is giraffes' species name, and it always begins with a (12) _______________________ case letter.
The history of the animal classification system can be (13) _______________________ back to the 18th century. Carl von Linné, a Swedish botanist, established taxonomy, the science of (14) _______________________ , (15) _______________________ , and naming all the organisms. He even gave himself a scientific name: Carolus Linnaeus!
Due to his hard work as well as other taxonomists' (16) _______________________ efforts, we have a well-structured classification system for not only animals, but also other living things on Earth.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper |
|
|
|
|
Please read this article and complete the following assignments in your journal
Vertebrate Classification: Phylum Chordata
By Cindy Grigg
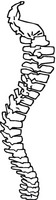 1 Biologists have described more than one million different kinds of living things on Earth. In order to study them, scientists divide them into groups based on similar traits. One system of classification divides all living things into five different kingdoms. They are animals, plants, fungi, monera, and protista. Some scientists use a six-kingdom system. This system divided monera into archaebacteria and eubacteria. 1 Biologists have described more than one million different kinds of living things on Earth. In order to study them, scientists divide them into groups based on similar traits. One system of classification divides all living things into five different kingdoms. They are animals, plants, fungi, monera, and protista. Some scientists use a six-kingdom system. This system divided monera into archaebacteria and eubacteria.
2 The kingdoms are then divided into five smaller groups: phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. The animal kingdom is divided into about thirty-five different phyla (plural of phylum), or major groups. The animal kingdom has more species than any other kingdom.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
3 Although a jellyfish and a person may not look very much alike, they belong to the same kingdom. People and jellyfish are both classified as animals. Animals are many-celled organisms that must obtain their food by eating other organisms. In addition, most animals reproduce sexually and can move from place to place. Biologists look for these characteristics in deciding whether an organism is an animal.
4 One important characteristic used to classify animals is whether or not they have a backbone or spine. An animal that does not have a backbone is called an invertebrate. Jellyfish, worms, spiders, and insects are all invertebrates. Most animal species are invertebrates (about ninety-five percent of all animals).
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
Assignment=CONTEXT CLUES - Please explain in your journal what the word"characteristic" mean in the paragraph above?
5 Vertebrates are all animals that have a backbone. Vertebrates are in the phylum Chordata. Members of this phylum are called chordates. Chordates share some common traits. At some point in their life cycle, they have a notochord, a nerve cord, and pharyngeal (fayr uhn JEE uhl) slits in the neck or throat. The notochord is a flexible rod that supports the animal's back. Lancelets are one chordate species that keep the notochord throughout their life cycle. Tunicates, on the other hand, have a notochord in the larval stage, but lose it when they reach the adult stage.
6 In most vertebrates, the notochord (part or all of it) is replaced by hard bone. Sharks are one type of vertebrate animal that have backbones made of cartilage. Cartilage is softer than bone. It is a connective tissue that is flexible and strong.
7 All chordates have a nerve cord that runs down their back. For example, your spinal cord connects your brain to your nerves so that electrical signals can move in both directions. Crustaceans and worms have nerve cords, but they don't run down their backs.
8 The third thing chordates have in common is slits in their throat area called pharyngeal slits. Fish keep their slits as part of their gills through their whole life cycle. Many vertebrates lose their slits before birth. Humans are one of these. The slits either close or develop into other structures, such as the jaw and the ear.
9 The backbone, or spine, is made up of small bones called vertebrae. These small bones have a hole in the center of them that the spinal cord runs through. The vertebrae have joints between them that allow flexibility. You can bend over to pick up something off the floor because of your flexible vertebrae.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the 4 short paragraphs above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
10 The backbone is part of a vertebrate's endoskeleton. An endoskeleton is inside the body. The endoskeleton supports and protects the body. It helps give it shape. It gives the muscles a place to attach. Part of the endoskeleton is the skull and ribs. The skull protects the brain. The ribs attach to the vertebrae and protect the internal organs, especially the heart and lungs.
Assignment=CONTEXT CLUES - Please explain in your journal what the word"internal" means in the paragraph above.
11 There are several advantages to having an endoskeleton. It grows as the animal grows. In contrast, arthropods (a group including crabs and caterpillars) have an exoskeleton. An exoskeleton is on the outside of the body. Some exoskeletons are hard, like a crab's shell. Some are leathery, like a caterpillar's. Animals with an exoskeleton must shed them as they grow larger. Have you ever found an empty insect exoskeleton?
12 In addition, an endoskeleton forms a frame that supports the body from the inside. This frame holds the body upright, against the pull of gravity. It also enables the animal to move easily. Because of these advantages of an endoskeleton, vertebrates can grow bigger than animals with an exoskeleton.
13 The chordate phylum is further divided into five classes. They are mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Vertebrate Classification: Phylum Chordata
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Vertebrate Classification: Phylum ChordataAssignment= In your journal, name several advantages to having an endoskeleton. Explain why they are advantages.
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Vertebrate Classification: Phylum ChordataAssignment= In your journal, summarize the main points of classification for vertebrates. What things do all vertebrates have in common?
Please copy this "cloze" assignment in your journal and complete it there
Vertebrate Classification: Phylum Chordata
By Cindy Grigg | | |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Biologists have described more than one million different kinds of living things on Earth. In order to study them, scientists (1) _______________________ them into groups based on similar traits. One system of(2) _______________________ (3) _______________________ all living things into five different kingdoms. They are animals, plants, fungi, monera, and protista. Some scientists use a six-kingdom system. This system(4) _______________________ monera into (5) _______________________ and (6) _______________________ . Biologists have described more than one million different kinds of living things on Earth. In order to study them, scientists (1) _______________________ them into groups based on similar traits. One system of(2) _______________________ (3) _______________________ all living things into five different kingdoms. They are animals, plants, fungi, monera, and protista. Some scientists use a six-kingdom system. This system(4) _______________________ monera into (5) _______________________ and (6) _______________________ .
The kingdoms are then divided into five smaller groups: phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. The animal kingdom is divided into about thirty-five different phyla (plural of phylum), or major groups. The animal kingdom has more species than any other kingdom.
Although a jellyfish and a person may not look very much alike, they belong to the same kingdom. People and jellyfish are both (7) _______________________ as animals. Animals are many-celled organisms that must obtain their food by eating other organisms. In addition, most animals (8) _______________________ sexually and can move from place to place. Biologists look for these (9) _______________________ in deciding whether an organism is an animal.
One important (10) _______________________ used to (11) _______________________ animals is whether or not they have a backbone or spine. An animal that does not have a backbone is called an invertebrate. Jellyfish, worms, spiders, and insects are all invertebrates. Most animal species are invertebrates (about ninety-five percent of all animals).
Vertebrates are all animals that have a backbone. Vertebrates are in the phylum Chordata. Members of this phylum are called chordates. Chordates share some common traits. At some point in their life cycle, they have a notochord, a nerve cord, and pharyngeal ((12) _______________________ uhn JEE uhl) slits in the neck or throat. The (13) _______________________ is a flexible rod that supports the animal's back. (14) _______________________ are one chordate species that keep the notochord throughout their life cycle. (15) _______________________ , on the other hand, have a notochord in the larval stage, but lose it when they reach the adult stage.
In most vertebrates, the notochord (part or all of it) is replaced by hard bone. Sharks are one type of vertebrate animal that have backbones made of cartilage. Cartilage is softer than bone. It is a connective tissue that is flexible and strong.
All chordates have a nerve cord that runs down their back. For example, your spinal cord connects your brain to your nerves so that electrical signals can move in both directions. Crustaceans and worms have nerve cords, but they don't run down their backs.
The third thing chordates have in common is slits in their throat area called pharyngeal slits. Fish keep their slits as part of their gills through their whole life cycle. Many vertebrates lose their slits before birth. Humans are one of these. The slits either close or develop into other structures, such as the jaw and the ear.
The backbone, or spine, is made up of small bones called vertebrae. These small bones have a hole in the center of them that the spinal cord runs through. The vertebrae have joints between them that allow flexibility. You can bend over to pick up something off the floor because of your flexible vertebrae.
The backbone is part of a vertebrate's endoskeleton. An (16) _______________________ is inside the body. The endoskeleton supports and protects the body. It helps give it shape. It gives the muscles a place to attach. Part of the endoskeleton is the skull and ribs. The skull protects the brain. The ribs attach to the vertebrae and protect the internal organs, (17) _______________________ the heart and lungs.
There are several advantages to having an endoskeleton. It grows as the animal grows. In contrast, arthropods (a group including crabs and caterpillars) have an exoskeleton. An exoskeleton is on the outside of the body. Some(18) _______________________ are hard, like a crab's shell. Some are leathery, like a caterpillar's. Animals with an exoskeleton must shed them as they grow larger. Have you ever found an empty insect exoskeleton?
In addition, an endoskeleton forms a frame that supports the body from the inside. This frame holds the body upright, against the pull of gravity. It also enables the animal to move easily. Because of these advantages of an endoskeleton, vertebrates can grow bigger than animals with an exoskeleton.
The chordate phylum is (19) _______________________ divided into five classes. They are mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please read this article and complete the following assignments in your journal
Animals Without Backbones
By Sheri Skelton | | |
 1 Feel the back of your neck. The bones at the back of your neck are connected to small bones all the way down the middle of your back. These bones make up your backbone. Scientists put all animals into two large groups. One group is animals with backbones. The other group is animals without backbones. 1 Feel the back of your neck. The bones at the back of your neck are connected to small bones all the way down the middle of your back. These bones make up your backbone. Scientists put all animals into two large groups. One group is animals with backbones. The other group is animals without backbones.
2 Animals without backbones are called invertebrates. Scientists estimate that 97 percent of all animals are invertebrates. They are found almost everywhere on Earth, living in oceans or freshwater ponds, living above the ground or under the ground. Invertebrates can be very tiny like the zooplankton, which are smaller than the head of a pin. Invertebrates can be very big like the giant squid, which can be over 30 feet long.
3 Insects are the biggest group of invertebrates. An insect's body has three parts: a head, a thorax, and an abdomen. An insect has an exoskeleton, or outer covering, to protect its body. The exoskeleton can't get bigger. When an insect grows, the insect has to shed its exoskeleton and grow a new one.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer
|
Assignment=CONTEXT CLUES - Please explain in your journal what the word"exoskeleton" means in the paragraph above.
4 Jellyfish are another kind of animal with no backbone. Jellyfish live in the ocean. Their bodies, which look like squishy blobs, are made up of over 90 percent water. Jellyfish have no hearts or brains. Long tentacles hang from their bodies. Jellyfish use the tentacles to catch food.
5 Starfish are another type of invertebrate. Scientists believe a better name for the starfish would be the sea star because the starfish is not really a fish. Starfish do not have blood or brains. If a starfish loses one of its limbs, the starfish can regenerate, or grow, another one.
6 Those are just a few of the different types of invertebrates. Many more kinds of animals without backbones are living all over the Earth.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the 3 short paragraphs above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Animals Without Backbones
1. | Invertebrates are animals without ______.


|
| |
| |
| |
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Animals Without BackbonesPlease explain in your journal in a 2-5 sentence paragraph, would you rather be a jellyfish or a starfish? Why?
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Animals Without BackbonesPlease explain in your journal in a 2-5 sentence paragraph, if you could be any insect, which one would you be? Write a story about what your life would be like as an insect.
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Animals Without BackbonesPlease explain in your journal in a 2-5 sentence paragraph what YOU think would be the benefits or advantages for being an invertebrate.
Please copy this cloze assignment in your journal and complete it there
Animals Without Backbones
By Sheri Skelton | | |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 Feel the (1) _______________________ of your neck. The bones at the back of your neck are connected to small bones all the way down the middle of your back. These bones make up your backbone. Scientists put all animals into two (2) _______________________ (3) _______________________ . One group is animals with backbones. The other group is animals (4) _______________________ backbones. Feel the (1) _______________________ of your neck. The bones at the back of your neck are connected to small bones all the way down the middle of your back. These bones make up your backbone. Scientists put all animals into two (2) _______________________ (3) _______________________ . One group is animals with backbones. The other group is animals (4) _______________________ backbones.
Animals without backbones are called invertebrates. Scientists estimate that 97 percent of all animals are (5) _______________________ . They are found almost everywhere on Earth, living in oceans or freshwater ponds, (6) _______________________ above the ground or under the ground. Invertebrates can be very tiny like the zooplankton, which are smaller (7) _______________________ the head of a pin. Invertebrates can be very big like the (8) _______________________ squid, which can be over 30 feet long.
Insects are the biggest (9) _______________________ of invertebrates. An insect's body has three parts: a head, a thorax, and an abdomen. An insect has an exoskeleton, or outer covering, to protect its body. The exoskeleton can't get bigger. When an insect grows, the insect has to shed its exoskeleton and grow a new one.
Jellyfish are another kind of animal with no backbone. Jellyfish live in the ocean. Their bodies, which look like squishy blobs, are made up of over 90 (10) _______________________ water. Jellyfish have no hearts or brains. Long tentacles hang from their bodies. Jellyfish use the tentacles to catch food.
Starfish are another type of (11) _______________________ . Scientists (12) _______________________ a (13) _______________________ (14) _______________________ for the starfish would be the sea star (15) _______________________ the starfish is not really a fish. Starfish do not have blood or brains. If a starfish loses one of its limbs, the starfish can (16) _______________________ , or grow, another one.
Those are just a few of the different types of invertebrates. Many more (17) _______________________ of animals without backbones are living all over the Earth.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Animals Without Backbones
1. | Invertebrates are animals without ______.


|
| |
|
4. | What do scientists believe would be a better name for the starfish?
 Sea urchin Sea urchin
 Sea star Sea star
 Ocean star Ocean star
 Sea fish Sea fish |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
|
|
|
| _____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ (Key 1 - Answer ID # 0379838) |
Make words by connecting the syllables.
dif | bone |
|
|
|
back | ti | ent |
|
|
oth | do | ton |
|
|
ab | plank | ter |
|
|
fresh | fer | mate |
|
|
mid | dle |
|
|
|
es | ter |
|
|
|
zoo | lieve |
|
|
|
pro | cause |
|
|
|
out | wa | men |
|
|
be | er |
|
|
|
bet | tect |
|
|
|
be | ant |
|
|
|
gi | er |
|
|
|
Please read this article and complete the following assignments in your journal
Six Kingdoms
By Cindy Grigg | | |
 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek scholar Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these large groups into smaller groups called subgroups. For example, plants were divided into trees, shrubs, or herbs. Animals were classified by how they moved. Animals that could fly were put into one subgroup. Animals that could swim were in another subgroup. Animals that walked, crawled, or ran were lumped into another subgroup. 1 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek scholar Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these large groups into smaller groups called subgroups. For example, plants were divided into trees, shrubs, or herbs. Animals were classified by how they moved. Animals that could fly were put into one subgroup. Animals that could swim were in another subgroup. Animals that walked, crawled, or ran were lumped into another subgroup.
Assignment=CONTEXT CLUES - Please explain in your journal what the word"classified" means in the paragraph above.
2 Nearly two thousand years later, the Swedish biologist Carolus Linnaeus created a different classification system. His idea was to group animals and plants based on similarities in their structures. For example, Linnaeus placed animals into groups based on whether or not they had a backbone. Like Aristotle, Linnaeus divided living things into two large groups - plants or animals. He called these groups "kingdoms." But today's scientists have tools and technology available to them that have allowed them to study organisms more closely. Scientists now realize that some organisms don't quite fit into the plant or animal group. As a result, several other kingdoms of organisms are now used. Today's scientists look at cell structure, how the organism moves, gets food, and reproduces.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
3 This is an explanation of the six kingdom classification system. First is the animal kingdom. Members of the animal kingdom are made up of many cells. Their cells have a nucleus that is contained inside a membrane. All animals get their food by eating other organisms. Animals are divided into two large subgroups: invertebrates (those without backbones) and vertebrates (those with backbones). Examples of vertebrates are fish, frogs, lizards, eagles, dogs, and people. Invertebrate animals include sponges, jelly fish, coral, insects, worms, and sea stars.
4 The plant kingdom's members are made of many cells that have an outer cell wall. They also have a membrane-bound nucleus. All plants make their own food by photosynthesis. Some groups of plants are ferns, mosses, conifers, and flowering plants. Mosses and ferns reproduce by spores. Conifers make seeds in cones. Flowering plants make seeds in their flowers. Some examples of plants are maple trees, pine trees, ferns, dandelions, moss, roses, and potatoes.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
5 The fungi kingdom contains single-celled or many-celled organisms that reproduce by spores. Fungi have cells that are surrounded by cell walls, like plants. In fungi, however, the cell walls are made of a different material. Fungi's cell walls are made of chitin, while plants' cell walls are made of cellulose. Fungi are different in another way from plants. Plants make their own food by photosynthesis by using chlorophyll. Fungi have no chlorophyll and so they cannot photosynthesize. Fungi must get their food by feeding on living or dead organisms. Many fungi are decomposers in the food chain. Examples of one-celled (unicellular) fungi are yeasts and some molds. Other fungi are mushrooms and puffballs.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer
|
6 The protist kingdom is made up of one-celled (unicellular) organisms and simple many-celled (multicellular) organisms. The nucleus of a protist's cell is enclosed in a nuclear membrane. Some protists, such as the one-celled amoeba and paramecium, feed on other organisms. Others, such as the one-celled euglena or the many-celled algae, make their food by photosynthesis. Other examples of the protist kingdom are diatoms and slime molds.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer
|
7 The archaebacteria kingdom includes single-celled organisms. The name means "ancient bacteria." Scientists think that these were like the first life forms on Earth billions of years ago. Their genetic material is not contained inside a nucleus. These cells are called prokaryotes. They lack other structures found in the cells of eukaryotes. Even though bacterial cells are lacking a nucleus and other structures, they still are able to perform all the tasks necessary for life. They use energy, grow and develop, respond to their environment, and reproduce. Some of the archaebacteria have been found in extremely hot water in geysers. They have been placed into a separate kingdom because their chemical makeup is different from the eubacteria. The way their genetic material reproduces is different as well.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
8 The sixth kingdom is the eubacteria. These, along with the archaebacteria kingdom, once made up the kingdom monera in the five-kingdom system of classification. Like the archaebacteria, eubacteria are one-celled and lack a nuclear membrane. Some are able to make their own food, and some must find food, also like the archaebacteria. Chemically they are similar to the other kingdoms, unlike the archaebacteria.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Six Kingdoms
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Six KingdomsIn your journal, please explain why do you think people try to group living things? In what ways is it useful? In what ways is it confusing? Please explain.
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Six KingdomsIn your journal, please explain why, do you think the scientific classification system will continue to change? Why or why not?
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Six KingdomsIn your journal, please name the characteristics that ALL animals share. In other words, what makes an animal an animal?
Please copy this cloze assignment in your journal and complete it there Six Kingdoms
By Cindy Grigg 
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek (1) _______________________ Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these large groups into smaller groups called (2) _______________________ . For example, plants were divided into trees, shrubs, or herbs. Animals were classified by how they moved. Animals that could fly were put into one subgroup. Animals that could swim were in another (3) _______________________ . Animals that walked, crawled, or ran were lumped into another subgroup. The first scientist to try to classify organisms was the Greek (1) _______________________ Aristotle. He classified living things as either plants or animals. Then he divided each of these large groups into smaller groups called (2) _______________________ . For example, plants were divided into trees, shrubs, or herbs. Animals were classified by how they moved. Animals that could fly were put into one subgroup. Animals that could swim were in another (3) _______________________ . Animals that walked, crawled, or ran were lumped into another subgroup.
Nearly two thousand years later, the Swedish biologist Carolus Linnaeus created a different classification system. His idea was to group animals and plants based on similarities in their structures. For example, Linnaeus placed animals into groups based on whether or not they had a backbone. Like Aristotle, Linnaeus divided living things into two large groups - plants or animals. He called these groups "kingdoms." But today's scientists have tools and technology available to them that have allowed them to study organisms more closely. Scientists now realize that some organisms don't quite fit into the plant or animal group. As a result, several other kingdoms of organisms are now used. Today's scientists look at cell structure, how the (4) _______________________ moves, gets food, and (5) _______________________ .
This is an (6) _______________________ of the six kingdom classification system. First is the animal kingdom. Members of the animal kingdom are made up of many cells. Their cells have a nucleus that is contained inside a membrane. All animals get their food by eating other organisms. Animals are divided into two large subgroups: invertebrates (those without backbones) and vertebrates (those with backbones). Examples of vertebrates are fish, frogs, lizards, eagles, dogs, and people. Invertebrate animals include sponges, jelly fish, coral, insects, worms, and sea stars.
The plant kingdom's members are made of many cells that have an outer cell wall. They also have a (7) _______________________ nucleus. All plants make their own food by photosynthesis. Some groups of plants are ferns, mosses, conifers, and flowering plants. Mosses and ferns reproduce by spores. Conifers make seeds in cones. Flowering plants make seeds in their flowers. Some examples of plants are maple trees, pine trees, ferns, dandelions, moss, roses, and potatoes.
The fungi kingdom contains single-celled or many-celled organisms that reproduce by spores. Fungi have cells that are surrounded by cell walls, like plants. In fungi, however, the cell walls are made of a different material. Fungi's cell walls are made of (8) _______________________ , while plants' cell walls are made of cellulose. Fungi are different in another way from plants. Plants make their own food by photosynthesis by using (9) _______________________ . Fungi have no chlorophyll and so they cannot (10) _______________________ . Fungi must get their food by feeding on living or dead organisms. Many fungi are decomposers in the food chain. Examples of one-celled (unicellular) fungi are yeasts and some molds. Other fungi are mushrooms and puffballs.
The protist kingdom is made up of one-celled (unicellular) (11) _______________________ and simple many-celled (multicellular) organisms. The nucleus of a protist's cell is enclosed in a nuclear membrane. Some protists, such as the one-celled (12) _______________________ and (13) _______________________ , feed on other organisms. Others, such as the one-celled euglena or the many-celled algae, make their food by (14) _______________________ . Other examples of the protist kingdom are diatoms and slime molds.
The archaebacteria kingdom includes single-celled organisms. The name means "ancient bacteria." Scientists think that these were like the first life forms on Earth billions of years ago. Their genetic material is not contained inside a nucleus. These cells are called prokaryotes. They lack other structures found in the cells of (15) _______________________ . Even though bacterial cells are lacking a nucleus and other structures, they still are able to perform all the tasks necessary for life. They use energy, grow and develop, respond to their environment, and (16) _______________________ . Some of the archaebacteria have been found in extremely hot water in geysers. They have been placed into a separate kingdom because their chemical makeup is different from the (17) _______________________ . The way their genetic material reproduces is different as well.
The sixth kingdom is the eubacteria. These, along with the archaebacteria kingdom, once made up the kingdom monera in the five-kingdom system of classification. Like the archaebacteria, eubacteria are one-celled and lack a nuclear membrane. Some are able to make their own food, and some must find food, also like the (18) _______________________ . Chemically they are similar to the other kingdoms, unlike the archaebacteria.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Six Kingdoms
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Use the letters from the scrambled word NEAMOR to form other words. Do not use the same letter more than once unless that letter is also in the scrambled word NEAMOR more than once.
|
| |
| |
|
| ______ | |
| |
|
| ______ | |
| |
|
| ______ | |
| |
|
| ______ | |
| | ______ | |
|
| ______ | |
| | ______ | |
|
| ______ | | ______ | |
| |
|
| ______ | | ______ | | ______ | |
| |
|
|
| | ______ | |
| | ______ | |
|
|
| | ______ | | ______ | | ______ | |
|
What is the Scrambled Word?
______ | | ______ | | ______ | | ______ | | ______ | | ______ | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please read this article and complete the following assignments in your journal
Endotherm or Ectotherm?
By Cindy Grigg | | |
 1 There are five major groups of vertebrate animals. Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are all vertebrates that share some common characteristics. They are different, too. One of these differences is the way their body temperature is controlled. 1 There are five major groups of vertebrate animals. Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are all vertebrates that share some common characteristics. They are different, too. One of these differences is the way their body temperature is controlled.
2 Mammals and birds have a body temperature that stays about the same no matter what the temperature of their environment is. Mammals and birds are called endotherms. An endotherm is an animal that can control its internal body temperature. Endotherms' body temperature is usually much warmer than the temperature of the environment and usually stays about the same temperature. Endotherms are called “warm-blooded” animals.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
3 The other three vertebrate groups are often called “cold-blooded” animals. This term is falling out of favor with scientists because it is misleading. They are called, instead, ectotherms. The blood of fish, amphibians, and reptiles is often warm. Their body temperatures are close to the temperature of their environment. If the environment is cold, the animal must move to a warmer place. If the environment is too warm, the animal must move into a cooler place.
4 For example, a seal is an endotherm. A seal's body temperature stays about the same, whether it is swimming in a cold ocean or lying in the sun on a beach. An alligator is an ectotherm. The alligator's temperature is higher when it is lying in the sun on a riverbank, and its body temperature is cooler when the alligator moves into cool water.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
5 How do endotherms regulate their body temperature? They have adaptations that help them do this. Sweat glands help keep endotherms cool. When an endotherm gets hot, the sweat evaporates and cools the animal's skin. Fur and feathers are another adaptation to regulate body temperature. These specialized skin coverings help the animals stay warm. Since ectotherms have a stable body temperature, they can live in a wide variety of environments. Ectotherms are more limited in their choice of environment because they are dependent on the environmental temperature.
Assignment=CONTEXT CLUES - Please explain in your journal what the word"regulate" means in the paragraph above.
6 Another adaptation to control body temperature that endotherms have is the ability to shiver. This involuntary movement of your muscles when you get cold burns calories. Heat is released. Shivering helps keep your body warm. This is an example of a metabolic way that endotherms can regulate their body temperature. However, this ability comes at a cost. Since energy must be used to maintain the animal's body temperature, more energy is required for the animal to live.
7 In contrast, ectotherms rely on behavior to regulate their body temperature. They must move their bodies into the shade or sun to cool down or warm up. This requires less energy than constant metabolic regulation. This is why many reptiles and other ectotherms can eat one large meal and not eat again for some time.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Endotherm or Ectotherm?
| |
3. | Which groups of vertebrate animals are ectotherms?


|
|
4. | Which groups of vertebrate animals are endotherms?


|
|
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Endotherm or Ectotherm?Assignment=Please explain in your journal in a 2-3 sentence paragraph are dogs endotherms or ectotherms? How do you know?
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Endotherm or Ectotherm?Assignment=Please explain in your journal in a 2-3 sentence paragraph what are some advantages and disadvantages of being endothermic.
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Endotherm or Ectotherm?Assignment=Please explain in your journal in a 2-3 sentence paragraph what are some advantages and disadvantages of being ectothermic.
Please copy this cloze assignment in your journal and complete it there
Endotherm or Ectotherm?
By Cindy Grigg | | |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 There are five major groups of (1) _______________________ animals. Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are all (2) _______________________ that share some common characteristics. They are different, too. One of these differences is the way their body temperature is controlled. There are five major groups of (1) _______________________ animals. Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals are all (2) _______________________ that share some common characteristics. They are different, too. One of these differences is the way their body temperature is controlled.
Mammals and birds have a body temperature that stays about the (3) _______________________ no matter what the temperature of their environment is. Mammals and birds are called endotherms. An endotherm is an animal that can control its internal body temperature. Endotherms' body temperature is usually much warmer than the temperature of the environment and usually stays about the same temperature. Endotherms are called “warm-blooded” animals.
The other three vertebrate groups are often called “cold-blooded” animals. This term is falling out of (4) _______________________ with scientists because it is misleading. They are called, instead, (5) _______________________ . The blood of fish, amphibians, and reptiles is often warm. Their body temperatures are close to the temperature of their environment. If the environment is cold, the animal must move to a warmer place. If the environment is too warm, the animal must move into a cooler place.
For (6) _______________________ , a seal is an (7) _______________________ . A seal's body temperature stays about the same, (8) _______________________ it is swimming in a cold ocean or lying in the sun on a beach. An alligator is an (9) _______________________ . The alligator's temperature is higher when it is lying in the sun on a riverbank, and its body temperature is cooler when the alligator moves into cool water.
How do endotherms regulate their body temperature? They have adaptations that help them do this. Sweat glands help keep endotherms cool. When an endotherm gets hot, the sweat evaporates and cools the animal's skin. Fur and feathers are another adaptation to regulate body temperature. These specialized skin coverings help the animals stay warm. (10) _______________________ ectotherms have a stable body temperature, they can live in a wide (11) _______________________ of environments. Ectotherms are more limited in their choice of environment because they are dependent on the environmental temperature.
Another adaptation to control body temperature that endotherms have is the ability to shiver. This involuntary (12) _______________________ of your muscles when you get cold burns calories. Heat is released. (13) _______________________ helps keep your body warm. This is an example of a metabolic way that endotherms can regulate their body temperature. However, this (14) _______________________ comes at a cost. Since energy must be used to maintain the animal's body temperature, more energy is required for the animal to live.
In contrast, ectotherms rely on (15) _______________________ to regulate their body temperature. They must move their bodies into the shade or sun to cool down or warm up. This requires less energy than constant metabolic (16) _______________________ . This is why many reptiles and other ectotherms can eat one large meal and not eat again for some time.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Symmetry in Animals
By Cindy Grigg | | |
 1 You probably know what symmetry means in math class. When a figure can be divided along a line or plane, and the two halves are congruent, we say it has symmetry. In nature, too, symmetry can be seen in plants and animals. One way biologists describe animals is the type of symmetry the animal's body has. Here are some of the different types of symmetry. 1 You probably know what symmetry means in math class. When a figure can be divided along a line or plane, and the two halves are congruent, we say it has symmetry. In nature, too, symmetry can be seen in plants and animals. One way biologists describe animals is the type of symmetry the animal's body has. Here are some of the different types of symmetry.
2 Animals with bilateral symmetry have one line that divides them into two mirror images. Look at a butterfly. If you drew a line exactly down the center of its body from its head to its tail, the two halves would be the same, but mirror images of each other. There is only one line of symmetry where this is true. In spite of the complexity of some butterflies' patterns, symmetry exists. People, dogs, cats, and elephants all have bilateral symmetry.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
3 Animals with radial symmetry have body parts arranged around a central point. Any line drawn from one side through the center to the opposite side will divide the animal into two symmetrical halves. Animals with radial symmetry have many lines of symmetry. Because of the circular arrangement of their parts, radially symmetrical animals do not have distinct front or back ends. They may have distinct top and bottom sides. Some examples of these animals are jellyfish, sea urchins, corals, and sea anemones. A bicycle wheel also has radial symmetry.
Please copy this main idea and detail graphic organizer in your journal and complete it there from the paragraph above.
 |
| Main Idea and Detail Graphic Organizer |
4 There are a few animals, like most sponges, that don't have any type of symmetry. These asymmetrical animals have very simple body plans. Sponges have no brains, nerve cells, or any internal organs. They are the simplest multicellular animals. The bodies of more complex animals have either radial or bilateral symmetry.
5 Animals with radial symmetry all live in water. Most of them can't move very quickly. They rely on water currents to bring food to them. One advantage of having radial symmetry is that the animal can get food from any direction.
6 Larger, more complex animals all have bilateral symmetry. They have very different front and back ends. Different parts of the body are specialized to do different jobs. Sense organs around the front end or head help bilaterally symmetrical animals find food. Bilateral symmetry also helps animals avoid enemies. Most animals you know have bilateral symmetry.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Symmetry in Animals
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Symmetry in AnimalsAssignment=please explain in your journal what symmetry is
____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Symmetry in AnimalsAssignment=please explain in your journal how can bilateral symmetry be an advantage to an animal? Explain in a 3-4 sentence paragraph
Please copy this assignment in your journal and complete it there Please copy this cloze assignment in your journal and complete it there
Symmetry in Animals
By Cindy Grigg | | |
Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension.
 You probably know what symmetry means in (1) _______________________ class. When a figure can be divided along a line or plane, and the two halves are congruent, we say it has symmetry. In nature, too, symmetry can be seen in plants and animals. One way biologists (2) _______________________ animals is the type of symmetry the animal's body has. Here are some of the different (3) _______________________ of symmetry. You probably know what symmetry means in (1) _______________________ class. When a figure can be divided along a line or plane, and the two halves are congruent, we say it has symmetry. In nature, too, symmetry can be seen in plants and animals. One way biologists (2) _______________________ animals is the type of symmetry the animal's body has. Here are some of the different (3) _______________________ of symmetry.
Animals with bilateral symmetry have one line that divides them into two mirror images. Look at a butterfly. If you drew a line exactly down the center of its body from its head to its tail, the two halves would be the same, but mirror images of each other. There is only one line of symmetry where this is true. In spite of the complexity of some butterflies' patterns, symmetry exists. People, dogs, cats, and elephants all have bilateral symmetry.
Animals with radial symmetry have body parts arranged around a (4) _______________________ (5) _______________________ . Any line drawn from one side through the center to the (6) _______________________ side will divide the animal into two symmetrical halves. Animals with radial symmetry have many lines of symmetry. Because of the (7) _______________________ (8) _______________________ of their parts, radially symmetrical animals do not have distinct front or back ends. They may have distinct top and bottom sides. Some examples of these animals are jellyfish, sea urchins, corals, and sea anemones. A bicycle wheel also has radial symmetry.
There are a few animals, like most sponges, that don't have any (9) _______________________ of symmetry. These asymmetrical animals have very simple body plans. Sponges have no brains, nerve cells, or any (10) _______________________ organs. They are the simplest (11) _______________________ animals. The bodies of more (12) _______________________ animals have either radial or bilateral symmetry.
Animals with radial symmetry all live in water. Most of them can't move very quickly. They (13) _______________________ on water currents to bring food to them. One advantage of having radial symmetry is that the animal can get food from any (14) _______________________ .
Larger, more complex animals all have bilateral symmetry. They have very different front and back ends. Different parts of the body are specialized to do different (15) _______________________ . Sense organs around the front end or head help bilaterally (16) _______________________ animals find food. Bilateral symmetry also helps animals avoid enemies. Most animals you know have bilateral symmetry.
Copyright © 2011 edHelper
_____________________________ |
| | Date ___________________ |
Symmetry in Animals
POST TEST | Read more about: |
|
Animal Classification QuizClick on the radio button in front of the correct answer. |
|
|
|
|
|
No comments:
Post a Comment